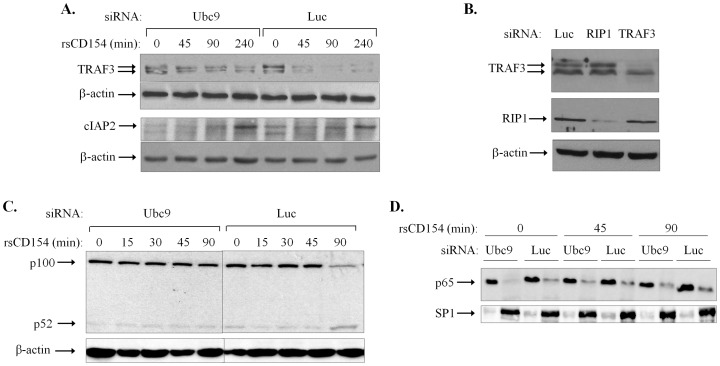
Figure 5. SUMOylation affects TRAF3 degradation and non-canonical NF-κB2 signaling in CD40-stimulated cells.
(A) Knock-down of Ubc9 diminishes CD40 ligand (CD154) induced TRAF3 degradation. EJ cells were transfected with Ubc9 siRNA or an unrelated siRNA targeting luciferase (Luc) prior to stimulation with 0,5 µg/ml recombinant CD154 and lysis. Lysates were immunoblotted with anti-TRAF3, anti-cIAP2 or anti-β-actin antibodies. Results are representative of at least 5 independent experiments. (B) Validation of siRNA targeting TRAF3. EJ bladder carcinoma cells were transfected with siRNAs against TRAF3, RIP1 or the unrelated luciferase and knock-down efficacy and specificity were determined by immunoblotting cell lysates with anti-TRAF3, RIP1 or β-actin antibodies. (C) Lysates from Ubc9 knocked-down cells were immunoblotted with anti-NF-κB2 mAb recognizing both the full-length p100 and processed p52 form of NF-κB2 or with β-actin as loading control. Results are representative of 3 independent experiments. (D) Nuclear and cytoplasmic protein extracts were prepared from control and Ubc9 siRNA-transfected EJ cells before and after stimulation with 0,5 µg/ml CD40L and analyzed for p65/RelA expression by immunoblot. The transcription factor Sp1 was used as a marker for the purity of the nuclear cell extract preparation. Results are representative of 3 independent experiments.