Figure 3. Modulating crb levels in the Aβ42 background leads to defects in axonal targeting from retina to the brain.
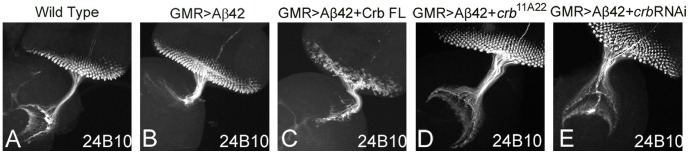
(A) Wild Type eye disc stained with sensory neuron marker, Chaoptin (24B10) [34], which marks only photoreceptor neurons and their axons. The photoreceptor neurons extends through the optic stalk and innervate the medulla and lamina of the larval brain. Note that misexpression of Aβ42 (GMR>Aβ42) in the eye imaginal discs, (B) there is mislocalization of 24B10 expression showing aberrant axonal targeting from retina to brain. The retinal axons fail to innervate the two layers of the brain and end abruptly. (C) Misexpression of Crb full length (FL) in the GMR>Aβ42 background (GMR>Aβ42+Crb FL) strongly enhances the neurodegeneration phenotype which results in (C) lack of axonal targeting from retina to brain. Reducing Crb levels by using (D) crb11A22 allele [33] (GMR>Aβ42+crb11A22) or (E) crb RNAi (VDRC) (GMR>Aβ42+RNAi) result in the significant rescue of GMR>Aβ42 mediated neurodegeneration as evident from the (D, E) restoration of retinal axon targeting.
