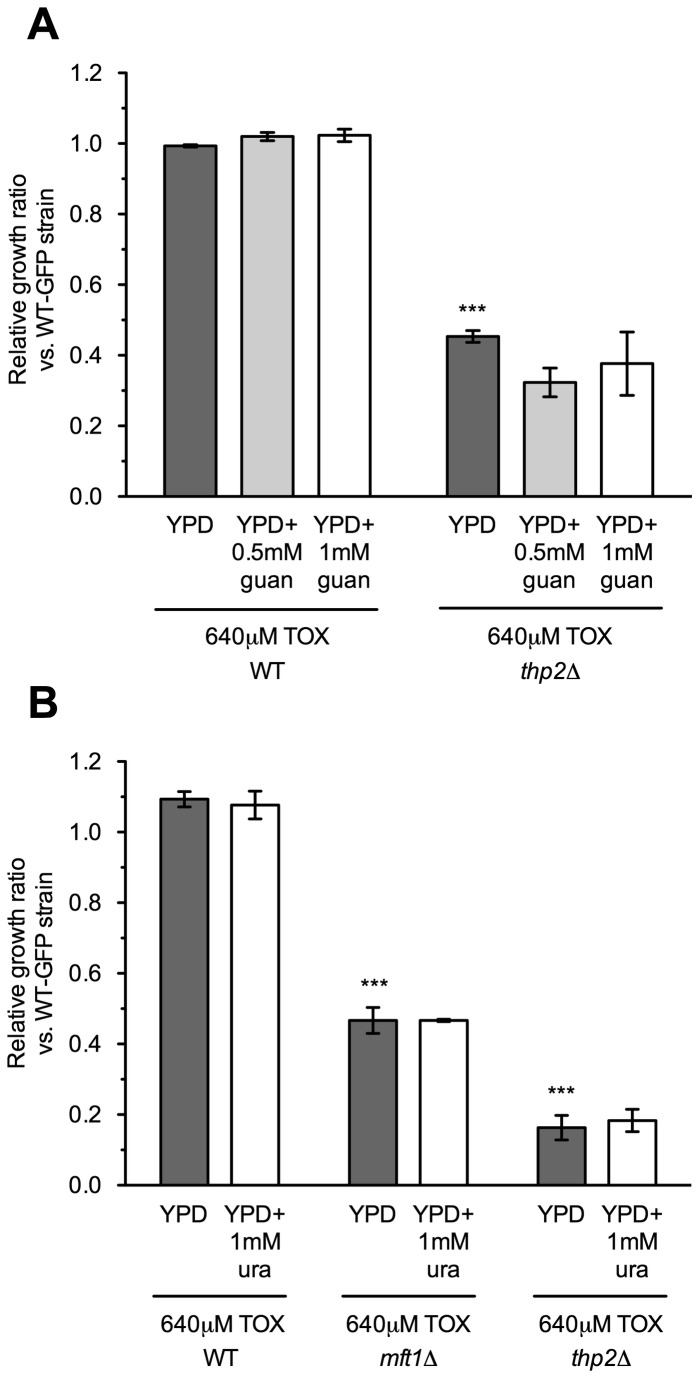
Figure 6. Neither guanine nor uracil rescues toxaphene sensitivity of transcription elongation mutants.
Relative growth ratios (treatment vs. control) to a GFP-expressing wild-type strain were obtained for three independent cultures and the means and SEs are shown. One-way ANOVA followed by a Bonferroni post-test determined statistical significance. ***p<0.001 for wild-type/mutant comparisons. (A) The toxaphene sensitivity of the thp2Δ strain cannot be rescued by guanine. YPD media was supplemented with the indicated concentrations of guanine and toxaphene. (B) Uracil cannot reverse the toxaphene sensitivity of the mft1Δ or thp2Δ strains. Uracil and toxaphene were added to YPD media at the indicated concentrations. The impact of toxaphene on mft1Δ and thp2Δ was stronger in these relative growth experiments versus growth curve assays (see Figure 3). Most likely, this is due to the competitive nature of the relative growth assays, where even in control experiments, deletions with intrinsic growth defects are outcompeted by wild-type. Exposure to toxaphene likely magnified the relative growth defects between mft1Δ or thp2Δ and the wild-type strain in this assay.