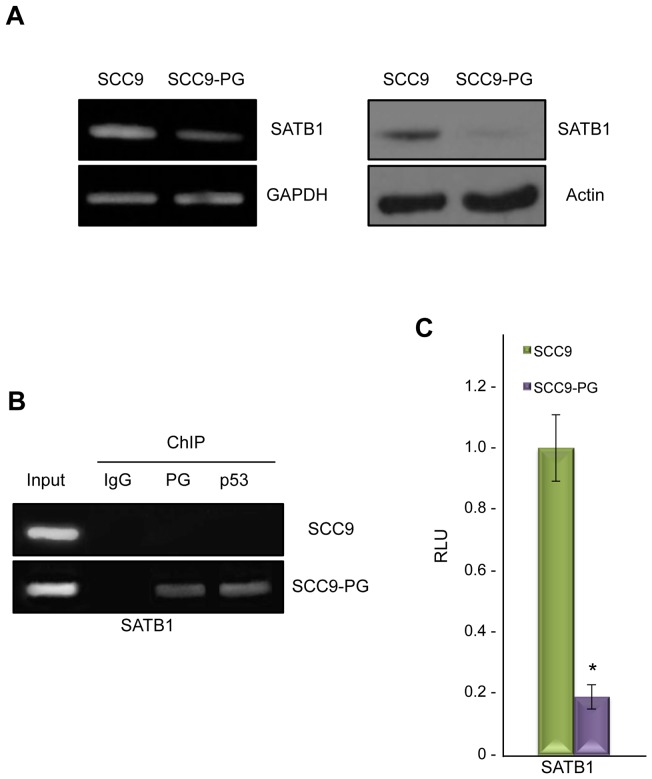
Figure 1. Plakoglobin associates with and suppresses the SATB1 promoter in SCC9-PG cells.
A. (Left) Total cellular RNA was isolated from SCC9 and SCC9-PG cells, reverse transcribed and processed for PCR using primers specific to SATB1 and GAPDH. (Right) Equal amounts of total cellular proteins from SCC9 and SCC9-PG cells were resolved by SDS-PAGE and processed for immunoblotting with antibodies to SATB1 and Actin. B. SCC9 and SCC9-PG cells were formaldehyde fixed and processed for chromatin immunoprecipitation. Following sonication, extracts were immunoprecipitated using control IgG, plakoglobin and p53 antibodies. Following extensive washes, immunoprecipitated DNA was separated from the immune complexes and purified using standard DNA purification protocols. The purified DNA was then processed for PCR using SATB1 primers. As a positive control, total cellular DNA (Input) was amplified using the same primers. C. SCC9 and SCC9-PG cells were transfected with luciferase reporter constructs under the control of a 1.2 kb sequence of the SATB1 promoter. Luciferase activities were measured 48 hours post-transfection. The levels of luciferase activities from the vector and SATB1 reporter constructs were determined from a minimum of three independent transfections and normalized for transfection efficiency by co-transfection with a β-galactosidase expression vector. The SATB1 promoter activity was normalized to the corresponding vector activity for each cell line and then normalized to SCC9 (*p<0.01). PG, plakoglobin; RLU, Relative Light Units.