Figure 1. Cloning of radmis gene.
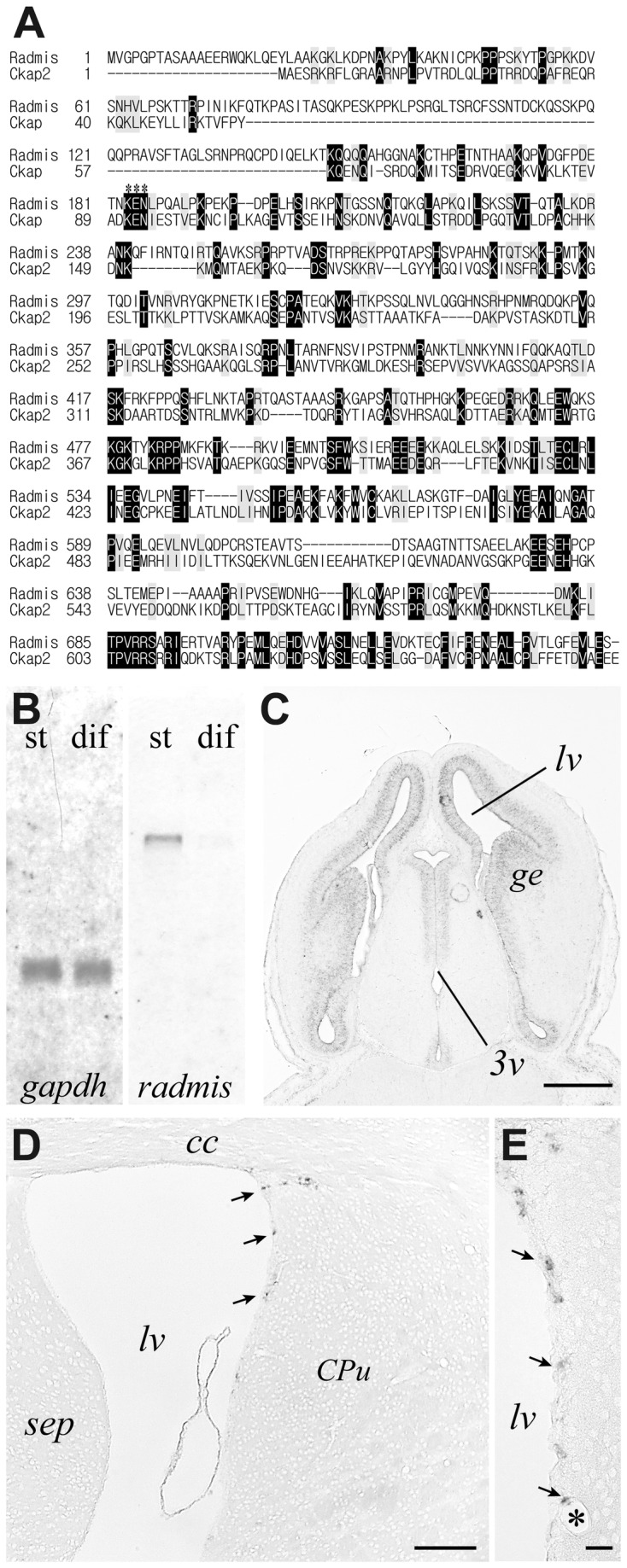
(A) Primary structure of mouse radmis, and the alignment with mouse ckap2 is shown. Identical amino acids are highlighted, and similar amino acid residues are shaded in gray. Gaps in the alignment are indicated by dashes. Asterisks denote the KEN box sequence. (B) Northern blot analysis. St, NSCs expanded in monolayer culture; dif, differentiating cells. Equal loading of RNAs was verified by probing with gapdh (right panel). (C-E) In situ hybridization for the radmis mRNA. Horizontal section of E 13.5 embryonic brain showing radmis expression in the VZ surrounding lateral ventricles (lv) and the 3rd ventricle (3v) (C). Coronal section of adult forebrain (D). Magnified view of the adult SVZ (E) showing each radmis-positive cell (arrows) sparsely distributed in the lateral wall SVZ of the lateral ventricle. Bars: C, 180 μm; D, 100 μm; E, 20 μm. lv, lateral ventricle; 3v, third ventricle; ge, ganglionic eminence; cc, corpus callosum; str, striatum; asterisk, blood vessel.
