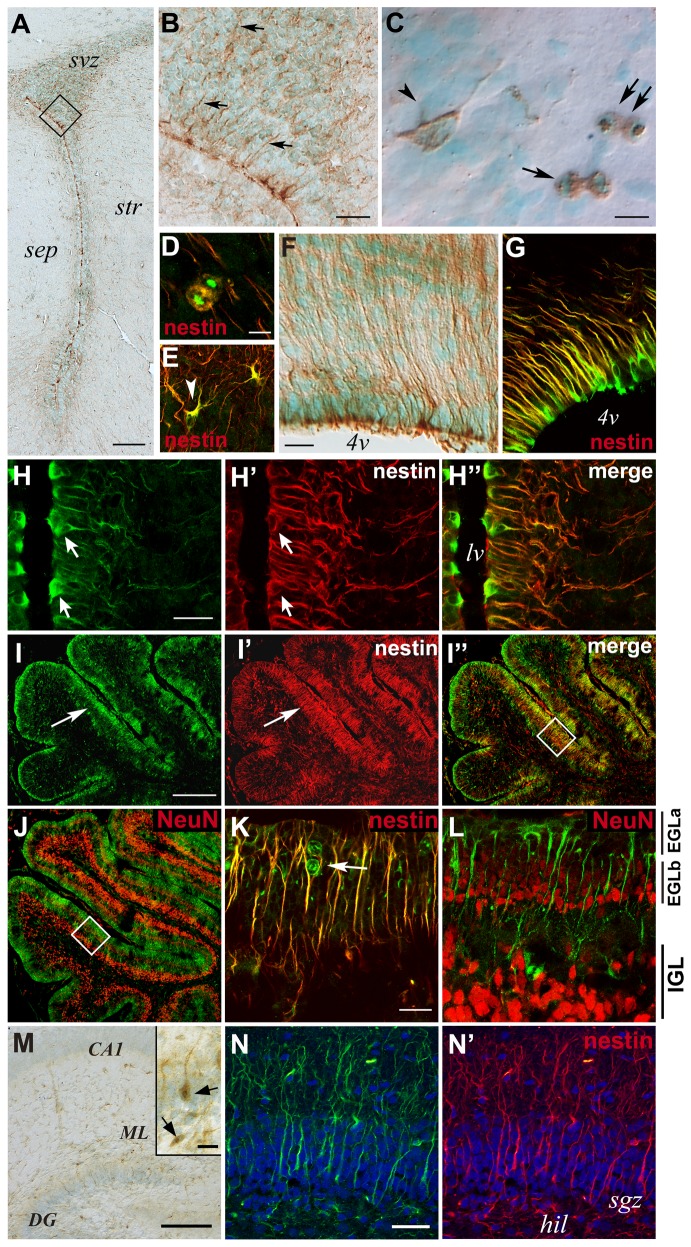
Figure 4. Radmis expression in postnatal brain.
(A–C) Coronal sections of P6 forebrain were immunostained for radmis (brown), followed by counterstaining with methyl green. (A) Low-power view of the SVZ region. (B) Magnification of the boxed area in A. Arrows indicate radmis immunoreactivity in fine processes extending from the lateral ventricle. (C) Individual radmis-positive cells within the SVZ. Radmis is detected in cells with short processes (arrowhead), or during mitosis (arrows). (D, E) Double immunostaining of SVZ cells for radmis (green) and nestin (red). (F, G) Pontine area surrounding the 4th ventricle and immunostained for radmis (F). (G) Double-immunostaining for radmis (green) and nestin (red). (H) Lateral and medial wall surrounding the lateral ventricle, stained for radmis (green) and nestin (red). Arrows indicate radmis expression in nestin-positive immature ependymal cells and their processes. (I–L) Radmis expression in the postnatal cerebellum. Double-immunofluorescence labeling of sagittal sections through the P6 cerebellum, with antibodies against radmis (green) and nestin or NeuN (red). (I) Co-immunostaining with nestin. Radmis is highly expressed in densely packed cells in the EGL (I, arrowheads), which also express nestin (I”). (J) Double-labeling showing non-overlapping localization of radmis and NeuN. NeuN expression is prominent in the IGL and is faint in the EGL. (K, L) Higher magnification of the boxed area in I and J, respectively. The EGL is toward the top of the panels. Radmis is highly expressed in mitotic cells (arrow) residing in the outer zone of the EGL (EGLa), whereas NeuN is expressed in differentiating post-mitotic neurons in the inner zone of the EGL (EGLb), in addition to the granule neurons in the IGL. Note that radmis is also expressed in the nestin-positive radial fibers of developing Bergmann glia, coursing through the EGL. (M, N) Radmis expression in the hippocampus at P7. (M) Low-power view showing the radmis expression (brown) in the CA and DG regions. Inset shows the magnified view of the radmis-positive cells in DG. Arrows indicate mitotic cells. (N, N’) Double immunostaining of the P7 DG with nestin. Radmis is expressed in nestin-positive cells bearing the radially aligned process through the developing granular layer. Scale bars: A, 100 μm; B, 30 μm; C–E, 5 μm; F, G, 10 μm; H, 12 μm; I, J, 140 μm; K, L, 20 μm; M, 100 μm; M inset, 20 μm; N, 30 μm. sep, septum; str, striatum; 4v, 4th ventricle; IGL, internal granule layer; EGL, external granule cell layer; CA1, pyramidal layer of CA1 region; DG, dentate gyrus; ML, molecular layer of DG; hil, hillus; sgz, subgranular zone.