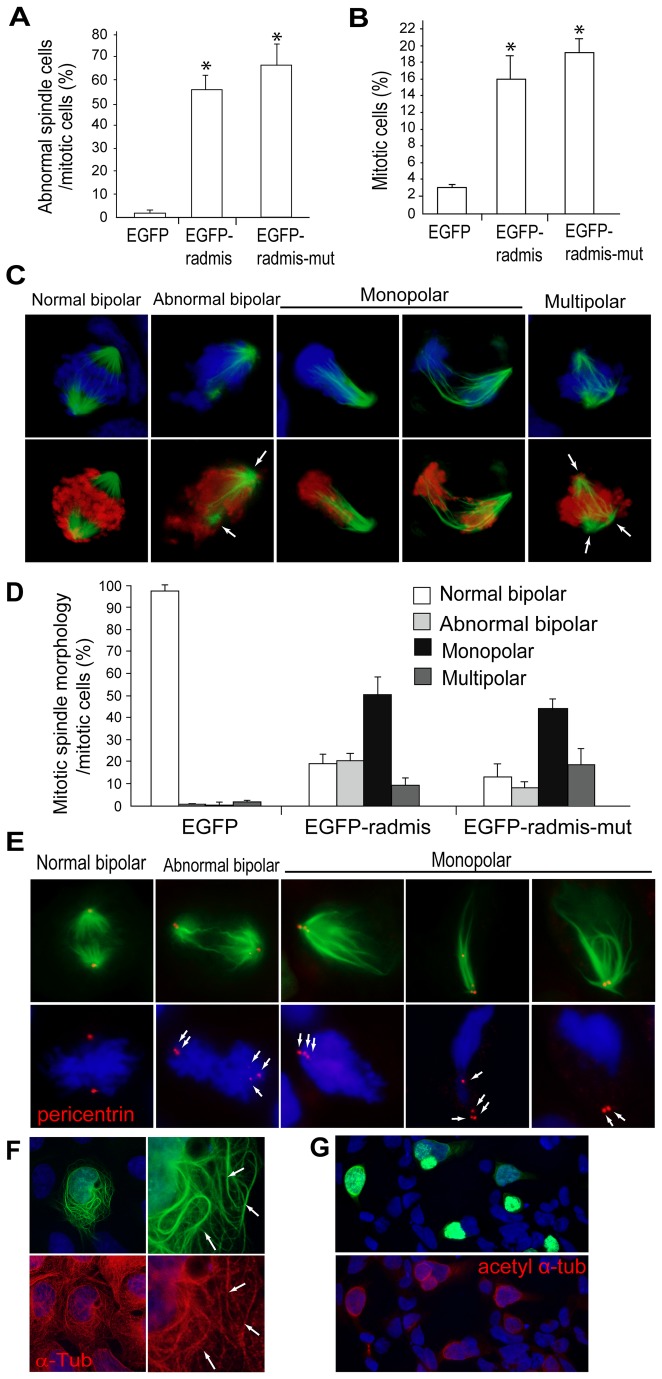
Figure 9. Radmis gain-of-function induces mitotic arrest accompanied by a mitotic spindle defect.
HEK293 cells were transfected with an EGFP-radmis, EGFP-radmis-mut, or EGFP control plasmid. At 44 h post-transfection, cells were fixed for analysis. (A) Quantification of cells exhibiting abnormal spindles among EGFP- and phosphoH3-positive mitotic cells. The morphology of mitotic spindles was analyzed by immunostaining for α-tubulin (data not shown). (B) Quantification of the mitotic index. The percentages of phosphoH3-positive mitotic cells among EGFP-, EGFP-radmis-, or EGFP-radmis-mut-transfected cells were calculated. (A, B) Data are obtained from four independent transfection experiments and presented as means ± SEM (%), and *p < 0.01 for EGFP control (Student’s t-test). EGFP-radmis (n = 428 cells), EGFP-radmis-mut (n = 370 cells), and control EGFP (n = 535 cells). . (C) Representative images of mitotic cells with aberrant spindles. Mitotic spindles observed in EGFP-radmis-transfected cells were categorized into normal bipolar, abnormal bipolar, monopolar, and multipolar. PhosphoH3 (red) and DNA (blue). An abnormal bipolar spindle is characterized by disorganized interpolar microtubules (arrows), and a multipolar spindle is characterized by extra spindle pole(s) (arrows). (D) Quantification of each type of mitotic spindle among EGFP-, EGFP-radmis-, or EGFP-radmis-mut-transfected cells. Data are obtained from six independent transfection experiments and presented as means ± SEM (%). EGFP (n = 97 mitotic cells), EGFP-radmis (n = 163 mitotic cells), EGFP-radmis-mut (n = 213 mitotic cells). (E) Centrosome labeled with an anti-pericentrin antibody (red) after radmis gain-of-function. Monopolar spindles in radmis-overexpressing cells were frequently accompanied by unseparated centrosomes. Arrows indicate centrosomes. DNA (blue). (F) Overexpression of EGFP-radmis induces microtubule bundling at interphase. Cytoplasmic microtubules in an interphase cell overexpressing EGFP-radmis (green) were visualized by α-tubulin staining (red). Right panels are higher magnifications showing radmis deposition in abnormally thick and winding or stiff microtubule bundles in the cytoplasm (arrows). (G) Cells transfected with EGFP-radmis (green) were immunostained for acetylated α-tubulin (red). Note that untransfected cells exhibit only a negligible level of acetylation of α-tubulin.