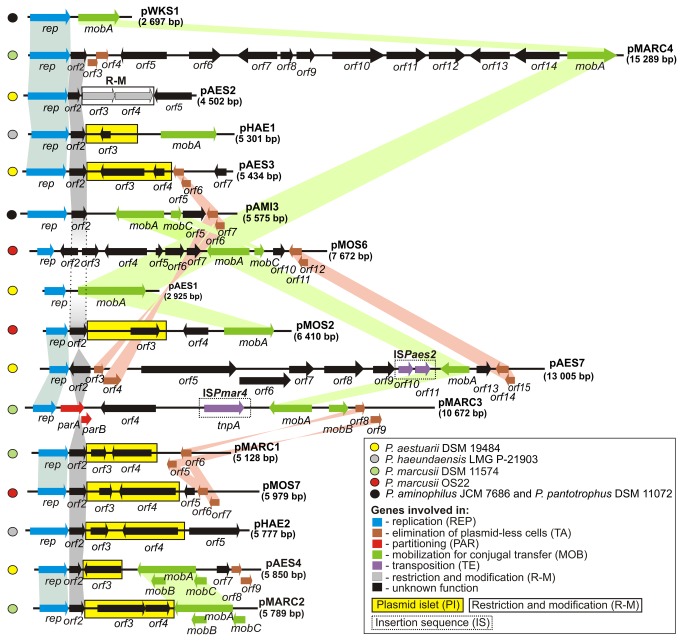
Figure 1. The genetic organization of the Paracoccus spp. plasmids analyzed in this study.
Arrows indicate the transcriptional orientation of the ORF2. The color-coded keys show the species and strain of origin of each plasmid (circles) and the likely plasmid maintenance/transfer processes in which the genes are involved (squares). Plasmid islets (PI) of lower than average G+C content, insertion sequences (IS) and restriction and modification systems (R-M) are indicated by the use of different boxes (see figure). Shaded areas connect genes of plasmids that encode orthologous proteins. For comparative analysis, two other related plasmids of Paracoccus spp. have been included: pAMI3 of P. aminophilus JCM 7686 [10] and pWKS1 of P. pantotrophus DSM 11072 [12].