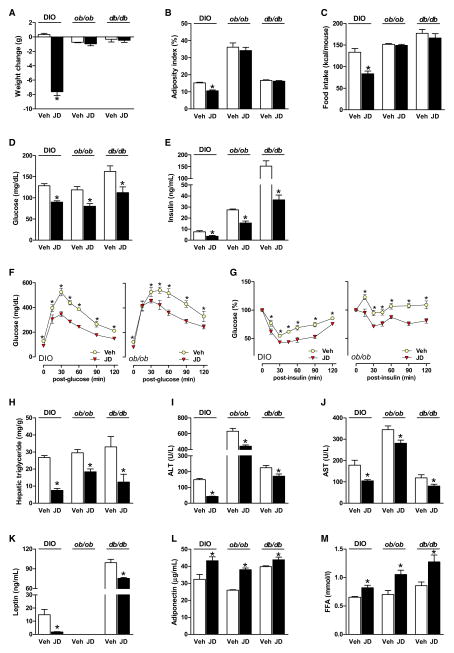
Figure 3. Metabolic Effects of JD5037 in DIO, ob/ob, and db/db Mice.
(A–C) JD5037 (3 mg/kg/day, 7 days) reduces body weight, adiposity, and food intake in DIO but not in ob/ob or db/db mice. *p < 0.05 relative to vehicle, n = 5–6 mice/group.
(D and E) JD5037 treatment attenuates the hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia in DIO, ob/ob, and db/db mice.
(F and G) JD5037 attenuates the glucose intolerance (ipGTT) and insulin resistance (ipIST) in DIO and ob/ob mice. *p < 0.5 relative to corresponding vehicle values.
(H–J) JD5037 reduces hepatic triglycerides, plasma ALT, and AST in all three strains.
(K) JD5037 attenuates hyperleptinemia in DIO and db/db mice, no plasma leptin in ob/ob mice.
(L and M) JD5037 causes similar increases in plasma adiponectin and FFA in DIO, ob/ob, and db/db mice.
For the lack of an acute hypophagic effect of JD5037 in a fasting/refeeding paradigm, see Figure S3, and for the lack of effect of JD5037 on daily food intake and body weight in CB1R−/− mice, see Figure S2. Vertical bars represent SEM.