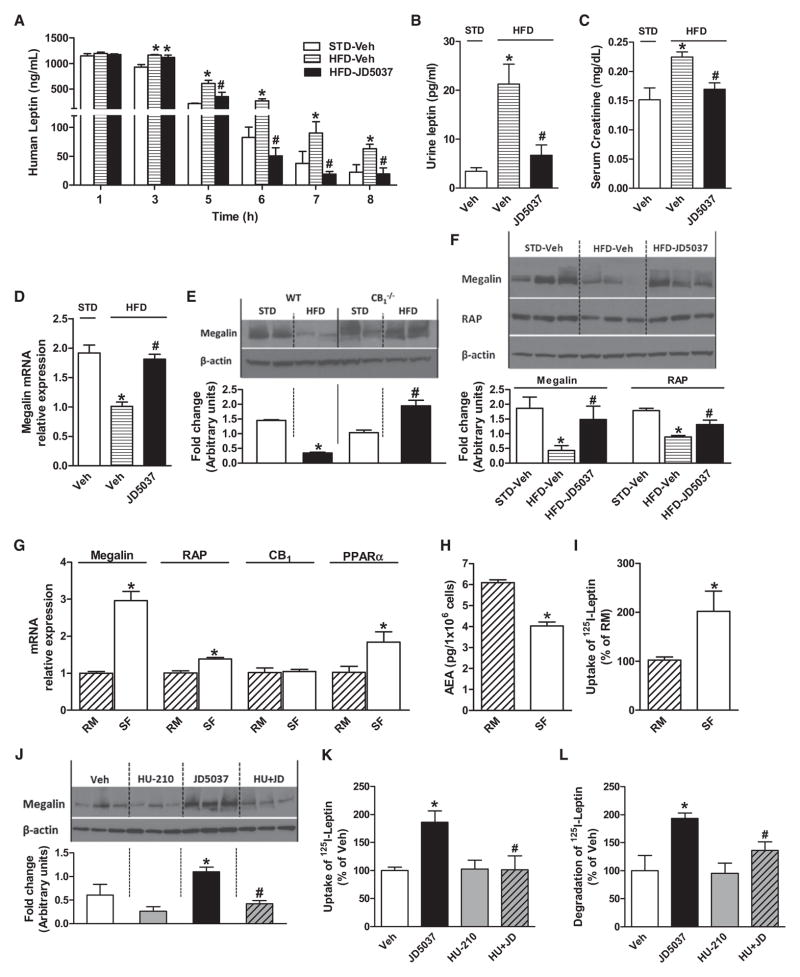
Figure 7. Reduced Leptin Clearance in DIO Mice Is Normalized by Peripheral CB1 Blockade.
(A) Pharmacokinetics of human leptin (10 mg/kg i.p.) injected into lean (STD-veh, t1/2 33.5 ± 0.1 min) and DIO mice (HFD-veh, t1/2 50.2 ± 4.8 min, p < 0.05) and DIO mice treated with JD5037, 3 mg/kg/day p.o. for 7 days (t1/2 28.8 ± 0.9 min). Note that the increase in t1/2 in DIO mice is reversed by JD5037, *p < 0.05 relative to STD, #p < 0.05 relative to HFD vehicle.
(B) Leptin microuria in DIO mice is reversed by JD5037 treatment, * and # as in (A).
(C) JD5037 reverses the diet-induced increase in serum creatinine levels, * and # as in (A).
(D) Reduction in megalin mRNA in kidney of DIO mice is reversed by JD5037 treatment.
(E) HFD reduces renal megalin protein in wild-type but not in CB1−/− mice (densitometry of western blots). *p < 0.05 relative to WT-STD, #p < 0.05 relative to CB1−/−-STD.
(F) Reduced megalin and RAP protein in the DIO kidney are normalized by JD5037, 3 mg/kg/day for 28 days, as quantified by densitometry * and # as in (A).
(G–I) Switching RPTEC from regular (RM) to serum-free medium (SF) increases megalin, RAP, and PPARα expression; reduces anandamide content; and increases leptin uptake.
(J–L) In RPTEC maintained in regular medium, JD5037 (1 μM, 24 hr) increases megalin protein levels, leptin uptake, and leptin degradation, effects reversed by coincubation with 100 nM HU-210. *p < 0.05 relative to vehicle, #p < 0.05 relative to JD5037.
For CB1/megalin interaction in the choroid plexus, see Figure S7. Vertical bars represent SEM.