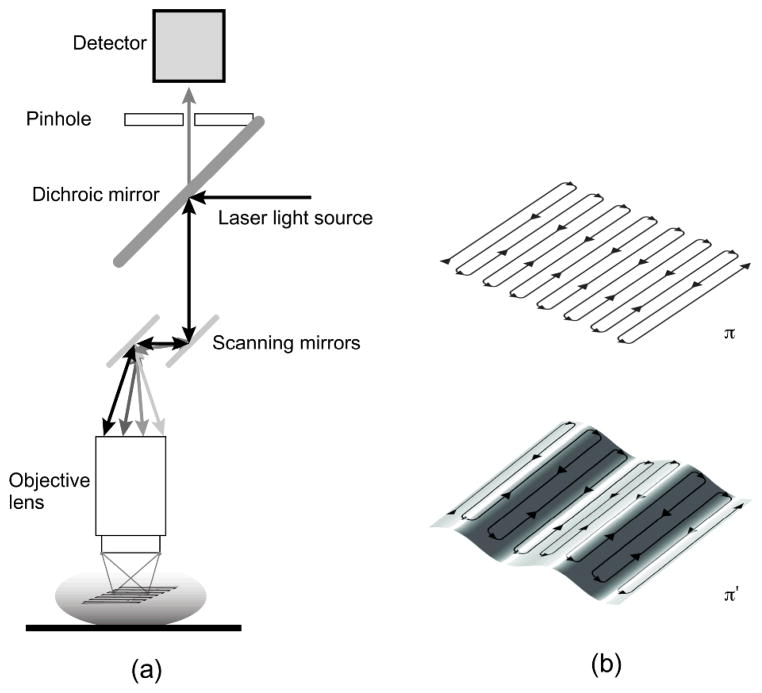
Fig. 5.
(a) Scheme of principle for laser scanning confocal microscopy. Two galvanometer mirrors oscillating on orthogonal axes scan the excitation laser beam along a raster path. Light is focused onto the sample and the emission light is descanned and detected through a dichroic mirror. (b) The raster scanning path lies on a horizontal imaging plane (top) perpendicular to the imaging objective. When the subject moves, the imaging plane in the organ’s reference frame will appear as a curved surface (bottom) modulated in time according to the motion periodicity. Reprinted with permission from [13]. © 2012 SPIE.