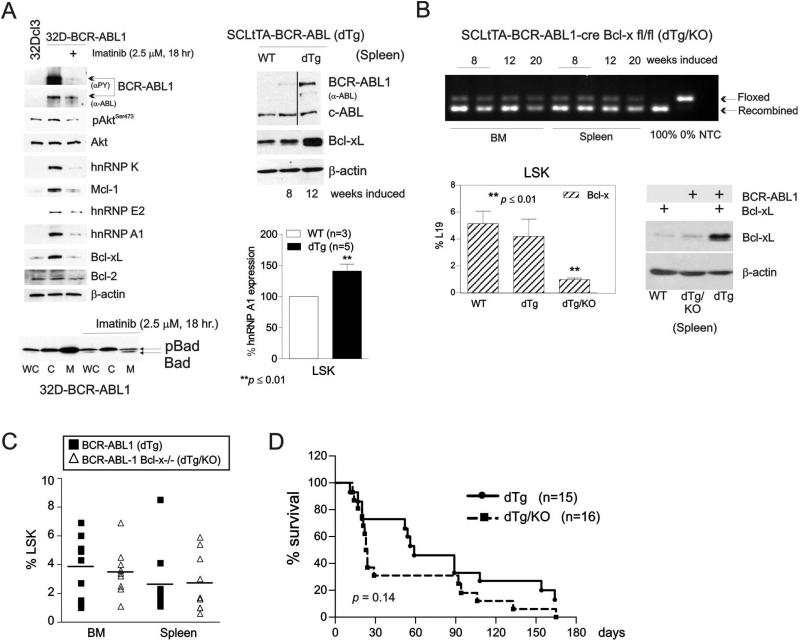
Figure 1. Expression of Bcl-xL is dispensable for BCR-ABL1-driven myeloproliferative disease (MPD) in vivo.
(A) Top left: Western blots show levels and/or activity of Mcl-1, Bcl-xL, Bcl-2, hnRNP K, hnRNP E2, hnRNP A1, total (α-ABL) and active (αPY) BCR-ABL1, and active Akt (pAktSer473) in parental, untreated and imatinib-treated BCR-ABL1-expressing myeloid progenitor 32Dcl3 cells. Top right: Bcl-xL and BCR-ABL1 protein expression in mononuclear cells (MNCs) from spleens of wild type (non-induced: WT) (lane 1) and leukemic SCLtTA-BCR-ABL1 (dTg) (lanes 2 and 3) mice. Bottom left: BAD expression in whole cell lysates (WC), cytoplasmic (C), and mitochondrial (M) subcellular fractions of untreated and imatinib-treated 32D-BCR-ABL1 cells. Bottom right: Flow cytometry analysis of hnRNP A1 expression in lineage-negative/Sca-1+/c-Kit+ (LSK) cells from the bone marrow of WT and 8-week induced dTg mice. (B) Top: PCR shows levels of recombination of Bcl-x floxed alleles in the bone marrow (BM) and spleen of 8, 12, and 20 week-induced SCLtTA-BCR-ABL1- cre Bcl-x fl/fl (dTg/KO) mice. Controls demonstrating complete recombination, absence of recombination, and the absence of a template (NTC) are shown in the last three lanes. Bottom left: bcl-x mRNA levels determined by Real-Time PCR in LSK cells from BM of WT and leukemic dTg and dTg/KO mice is reported as percentages of L19 expression. Results are given as mean ± Standard Error of the Mean (SEM); n = 3. Bottom right: Levels of Bcl-xL protein in MNCs from spleen lysates of WT, leukemic dTg/KO, and dTg mice. (C) Left: Frequency by flow cytometry of lineage-negative/Sca-1+/c-Kit+ (LSK) cells in BM and spleen of dTg and dTg/KO mice. (D) Kaplan-Meier plot shows survival times of dTg and dTg/KO leukemic mice. Asterisks (*) indicate statistical significance.