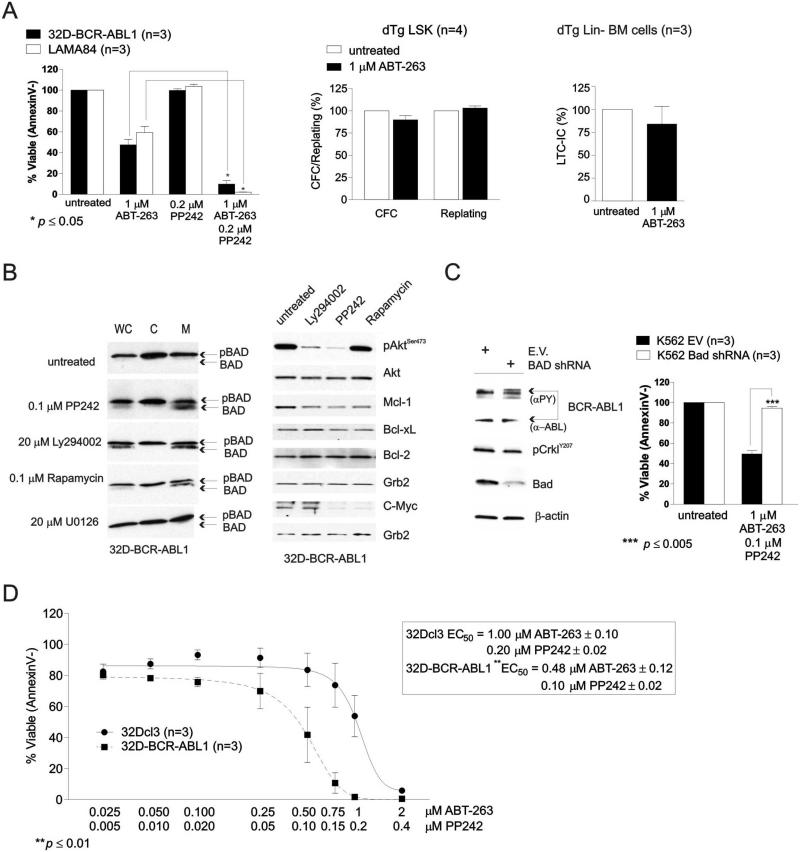
Figure 3. Inhibition of Bcl-xL triggers apoptosis of BCR-ABL1+ myeloid progenitors and is potentiated by reactivation of BAD.
(A) Left: Plot shows effect of ABT-263 and PP242 used alone or in combination on survival (expressed as the mean ± SEM of the percentage of AnnexinV− cells; n=3) of untreated and drug-treated 32D-BCR-ABL1 (black bars) and LAMA84 (white bars) cells; middle: Methylcellulose-based clonogenic potential and replating efficiency of untreated and ABT-263-treated LSK cells from spleens of dTg mice; right: effect of ABT-263 treatment on the long-term culture-initiating cell frequency in lineage-negative (Lin−) cells from BM of 8 week-induced dTg mice. (B) Levels of the active (BAD) and inactive (pBAD) BAD (left panels) and of Akt, Mcl-1, Bcl-xL, Bcl-2, and c-Myc in whole cell (WC) and cytoplasmic (C) and mitochondrial (M) subcellular fractions (left panels) and total lysates (right panels) of 32D-BCR-ABL1 cells untreated or treated with the indicated chemical inhibitors of known survival/proliferation pathways. (C) Right: Survival analysis shows that shRNA-mediated BAD downregulation suppresses the potentiating killing activity of PP242 in ABT-263-treated K562 cells. Left: Western blot shows downregulation of BAD by shRNA. Levels of total (α-ABL) and active (αPY) BCR-ABL1, pCrklY207, and in empty vector (EV) and BAD shRNA-expressing K562 cells are shown as controls. (D): Annexin V-staining shows effect of increasing doses of ABT-263/PP242 combination on survival of parental (solid line) and BCR-ABL1-expressing 32Dcl3 cells (dashed line). Inset shows EC50 values for 32Dcl3 and 32D-BCR-ABL1 cells. All data are representative of at least three independent experiments.