Figure 6.
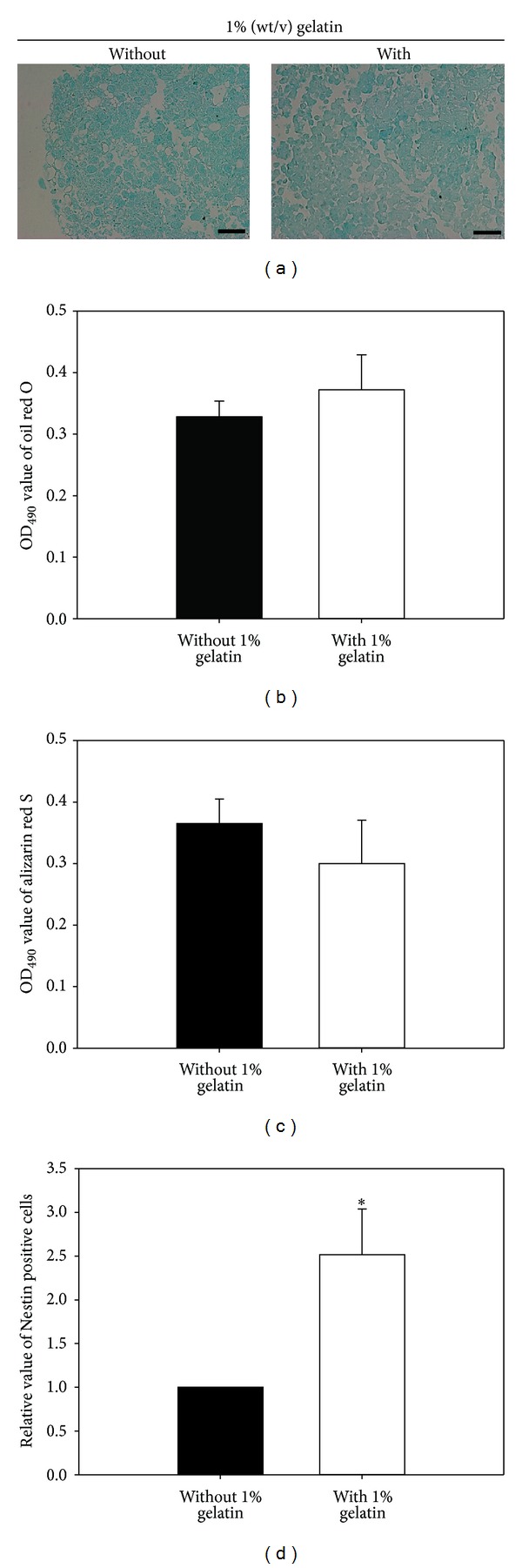
Effects of gelatin-coated matrix on the differentiation potential of BM-MSCs. By passage 5, BM-MSCs were cultured on dishes coated without or with 1% (wt/v) gelatin. (a) For analysis of chondrogenic differentiation potential, BM-MSCs were cultured on a 1% (wt/v) gelatin matrix using a chondrogenesis differentiation kit for 3 weeks, and differentiation into chondrocytes was assessed by alcian blue staining. (b) For analysis of adipogenic differentiation potential, BM-MSCs were incubated for 3 weeks in adipogenic differentiation medium. BM-MSCs that differentiated into adipocytes were identified by Oil red O staining and quantified by measuring the absorbance at 490 nm. There was no significant difference in adipogenic differentiation potential between BM-MSCs cultured without and with 1% (wt/v) gelatin. (c) For analysis of osteogenic differentiation potential, BM-MSCs were incubated in osteogenic differentiation medium for 2 weeks. BM-MSCs that differentiated into osteoblasts were identified by alizarin red staining (ARS), which stains calcium deposits in the differentiated cells, and quantified by measuring the absorbance at 550 nm. There was no significant difference in osteogenic differentiation potential between BM-MSCs cultured with and without 1% (wt/v) gelatin. (d) For analysis of neurogenic differentiation potential, BM-MSCs were cultured for 7 days in neurogenic differentiation medium. BM-MSCs that differentiated into neurogenic cells were stained with a fluorescence-conjugated primary antibody against Nestin (neural lineage marker) and assessed by flow cytometry. A significantly higher percentage of Nestin-positive cells was detected in BM-MSCs cultured on 1% (wt/v) gelatin matrix than in those cultured on plates without gelatin. All data shown are means ± S.D. of three (d) or four ((b) and (c)) independent experiments. *P < 0.05. Scale bar, 50 μm.
