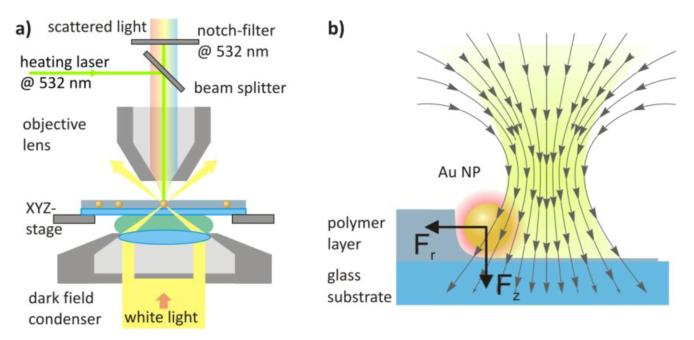
Figure 1.
Optically driven golden nano-burner. a) Diagram of the experimental setup. A microscope equipped with dark-field illumination via an oil immersion condenser (Zeiss Axiotech 100) is adapted to include the manipulation laser (Millenia Vs 532nm, Spectra-Physics). An air objective (Epiplan, Zeiss, 100x, NA 0.9) is used to simultaneously collect scattered light and focus the manipulation laser onto the sample. The sample position is controlled with piezo-driven stepper motor translation stages (Linos). Images are acquired using a digital camera (Canon EOS 550D). Scattering spectra are acquired using a spectrometer (Andor SpectraPro-300i) equipped with a CCD camera (Roper Scientific 1340/400). (b) Schematic representation of the optical forces acting on a nanoparticle inside a polymer layer during the patterning process. The laser beam is focused slightly above the substrate to utilize the radial optical force component of a divergent laser beam.