Figure 1.
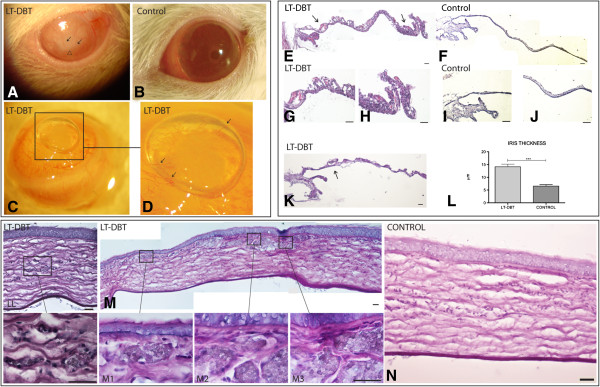
Anterior segment vessels. A: picture of in vivo 110-week-old animal (LT-DBT). The eye shows vessels in the cornea (arrow) and cataract (arrow head). B: in vivo 110-week-old control animal. C: gross section from an enucleated LT-DBT eye with an air bubble in the anterior chamber. D: Magnification from the C photograph showing the presence of vessels in the cornea (arrow). Light microscopy, PAS and eosin (E, G, H, K) and haematoxylin and eosin (F, I, J) iris staining from a LT-DBT animal (E, G, H, K). Arrows indicate the presence of abnormal vessels in the iris. F, I and J: control iris from a non-diabetic age-matched rat. Bar 20 μm. L: The iris thickness is higher in the LT-DBT rats represented in μm. ***p < 0.0001, LT-DBT mean 14.11 ± 1.010 (N = 50), control mean 6.557 ± 0.5647 (N = 47). Light microscopy; haematoxylin and eosin and PAS and eosin stained corneas. LL and M: vessels in the corneal stroma of LT-DBT animals, LL1 and M1, 2 and 3 are magnification of vessels within the corneal stroma. N: normal control cornea from a LT-Control rat. Bar 20 μm.
