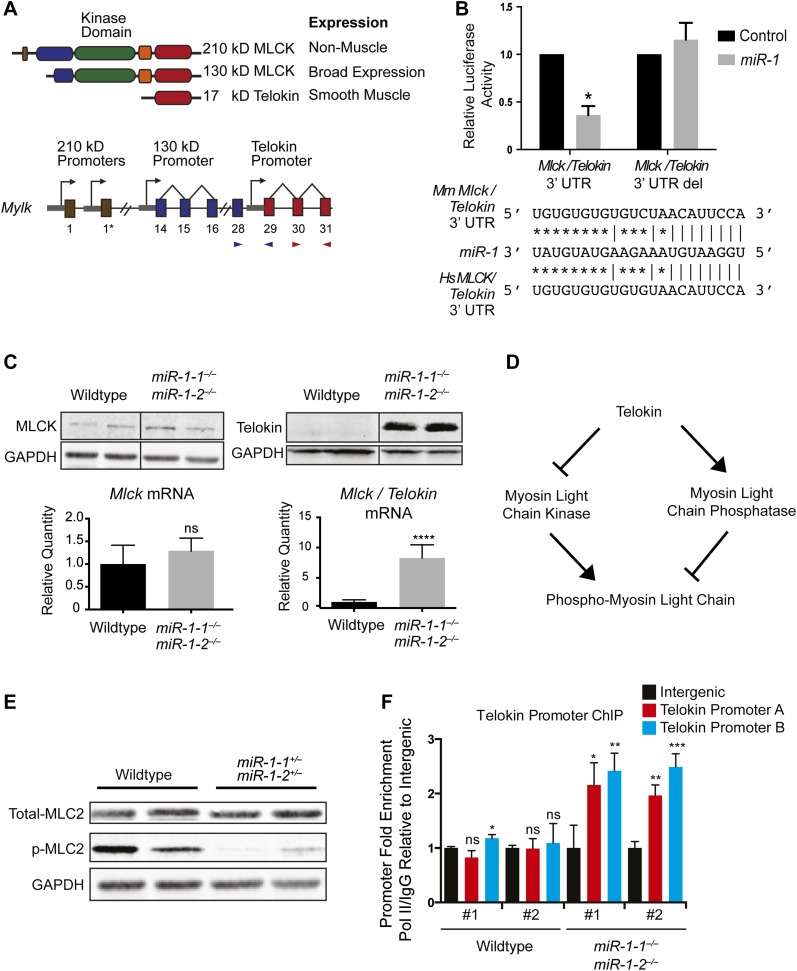
Figure 5. Dysregulation of Telokin and Myosin light chain phosphorylation in miR-1 null hearts.
(A) Diagram of the gene products encoded within the Mylk locus. Independent promoters preceding exons are indicated by arrows. Exon-spanning qPCR primers used are indicated in red (Mlck/Telokin) or blue (Mlck). (B) Luciferase activity of a reporter construct containing ∼200 bp of the Mlck/Telokin 3′-UTR surrounding the predicted miR-1 binding site with or without the site deleted. The constructs were co-transfected into H9C2 myoblasts with a miR-1 mimic or a control mimic. Sequence of the putative miR-1 target site as predicted by Targetscan and site conservation between human (Hs) and mouse (Mm) is indicated. (C) Western blot of heart lysates (top) and qPCR of RNA (bottom) from P0 wild-type or miR-1 null mice. (N = 5 per group). (D) Model of Telokin function in smooth muscle to promote the activity of myosin light chain phosphatase and inhibit the activity of the myosin light chain kinase. (E) Western blot of total myosin light chain 2 (MLC2) and phosphorylated myosin light chain (p-MLC2) in P0 wild-type or miR-1 null hearts; GAPDH serves as loading control. (F) qPCR of the Telokin promoter sequence or an intergenic genomic sequence following chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) of RNA polymerase II in P2 wild-type or miR-1 null hearts. For the Telokin promoter, two non-overlapping probe sets were used, indicated as Telokin promoter A and B.
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. Putative miR-1 targets dysregulated in miR-1 null hearts were not affected in miR-133a double-knockout hearts.