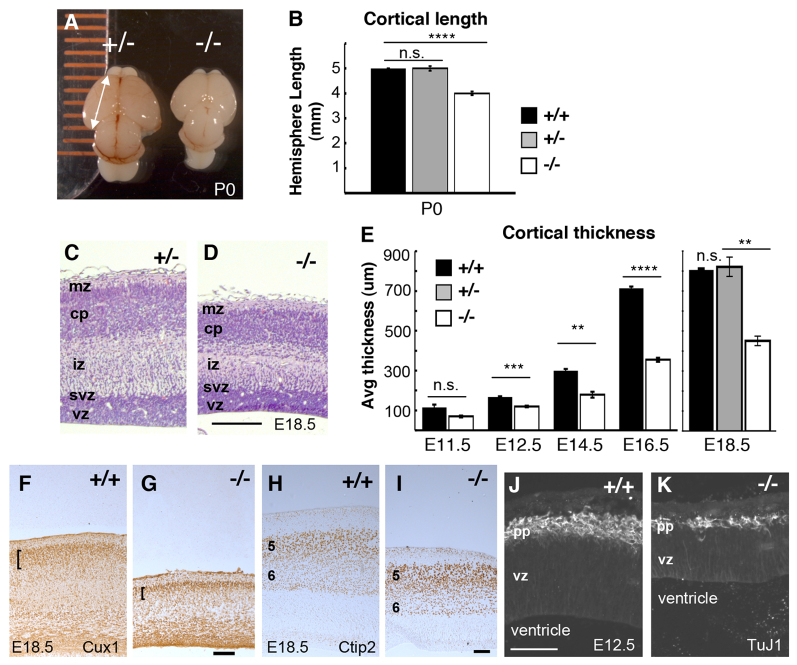
Fig. 1.
magoo mutant cortex has reduced length and thickness but preserved layer structure. (A) Dorsal view of heterozygous control (+/-) and magoo mutant (-/-) newborn [postnatal day (P) 0] mouse cortices. (B) The average length (mm) ± s.e.m. of eight wild-type (+/+), 20 heterozygous and 24 mutant P0.5 cortical hemispheres. ****P<1.0×10-8; n.s., not significant. (C,D) Cortical sections from comparable levels of control and homozygous magoo mutant littermates stained with H&E. In the mutant, cortical layers are thinner but positioned normally as marginal zone (mz), cortical plate neurons (cp), intermediate zone (iz), subventricular zone (svz) and ventricular zone (vz). (E) The average cortical thickness (μm) ± s.e.m. of magoo mutants is less than that of controls at all ages tested. Number of brains of each genotype: E11.5, 2; E12.5 and E14.5, 4; E16.5, 5; E18.5, 2. **P≤0.01, ***P<0.005, ****P<0.0001. (F,G) Cux1+ cells are present in superficial layers of both control and magoo mutant caudal cortex sections (brackets). (H,I) Ctip2 immunostaining on sections of middle cortex shows that cortical layers 5 and 6 are distinguishable and in the correct order in magoo mutants. (J,K) At E12.5, the preplate (pp) and vz are both thinner in mutants, but positioned normally. TuJ1 labels neuronal tubulin. Scale bars: 100 μm.