Fig. 3.
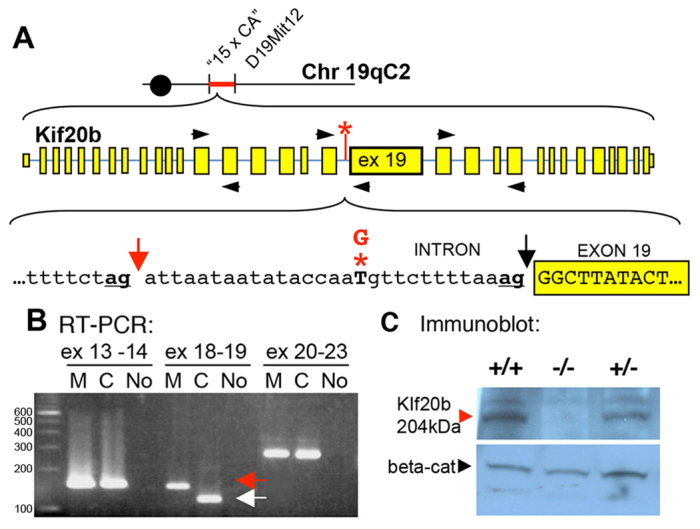
magoo is a splice mutant of Kif20b in which Kif20b protein is reduced to an undetectable level. (A) The magoo mutation was mapped between microsatellite markers ‘15 x CA’ and D19Mit12. magoo carries a T-to-G mutation (red asterisk) 13 bases upstream of exon 19 of Kif20b. This disrupts the normal splice acceptor (black arrow) and favors the ‘ag’ 29 bp upstream (red arrow). (B) RT-PCR detects aberrant splicing of Kif20b exon 19 in magoo mutants. Primers (black arrowheads in A) were designed to span splice sites between exons 13 and 14, 18 and 19, and 20 and 23. The exon 18-19 primers amplified a larger band from mutant cDNA (red arrow) than from the control (white arrow). Identical results were seen in three independent experiments. M, mutant; C, control; No, no template cDNA; ex, exon. (C) Immunoblot with antiserum recognizing the N-terminus of mouse Kif20b detects a 204 kDa band in brain lysates from +/+ and +/- E12.5 embryos, but not -/- embryos, even after film overexposure. Anti-β-catenin (beta-cat) is a loading control.
