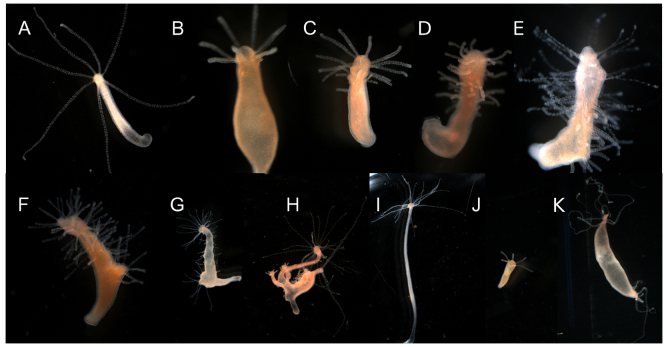
Fig. 2.
Chronic exposure to DAC-2-25 leads to ectopic tentacle formation that spreads towards the aboral end of the polyp. Hydra morphology before (A) and after (E) 3 weeks of exposure to 5 μM DAC-2-25; all pictures are of the same animal. Seven tentacles can be seen on the untreated animal (A). After 9 days of exposure the animal has produced two ectopic tentacles (B). After 13 days of exposure (C) and 16 days of exposure (D), the animal has an increased number of tentacles. After 21 days of exposure (E) the animal is covered in tentacles. This animal was then removed from DAC-2-25 and placed in HM. Tentacles were gradually lost, as seen after 8 days (F) and 12 days (G). Buds formed normally in the recovering animal (H) and had normal morphology upon detachment from the parent (J). After 54 days (I), the animal had re-established its original axial pattern. (K) Hydra morphology after 3 weeks of exposure to 50 nM ALP.