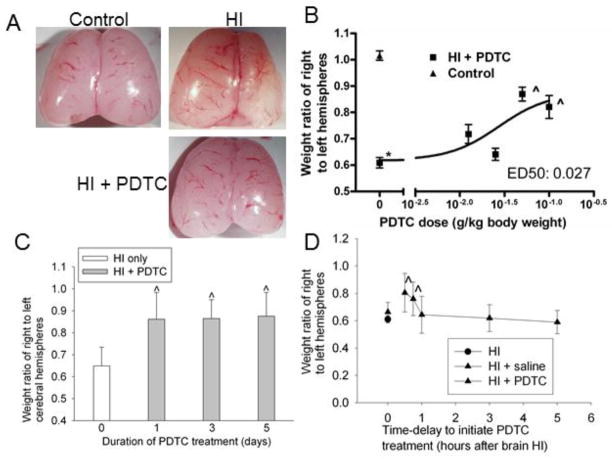
Fig. 1.
Neuroprotective effects of PDTC. Seven-day old rats were subjected to or were not subjected to the brain HI (right common carotid ligation plus 2-h hypoxia at 8% oxygen). Brain was harvested at 7 days after the brain HI. A: representative brain images of a control rat, rat with the HI only and rat with HI and then treated with 50 mg/Kg PDTC intranasally once a day for 3 days with the first dose at 15 min after the brain HI. B: dose-response. Various doses of PDTC were applied intranasally once a day for 3 days with the first dose at 15 min after the HI. Results are means ± S.D. (n = 5–7). * P < 0.05 compared with control rats. ^ P < 0.05 compared with rats that had brain HI only. C: Duration of treatment. Seven-day old rats were subjected to the brain HI and intranasal application of PDTC (50 mg/kg once a day) for various durations with the first dose at 15 min after the HI. Results are means ± S.D. (n = 4–7). ^ P < 0.05 compared with rats that had brain HI only. D: Time-window of treatment. Seven-day old rats were subjected to the brain HI and intranasal application of PDTC (50 mg/kg) at various times after the HI. One dose of PDTC was applied to the rats. Results are means ± S.D. (n = 4–12). ^ P < 0.05 compared with rats that had brain HI only.