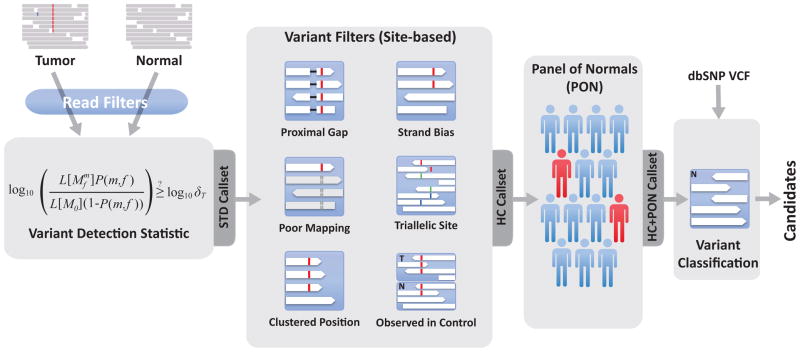
Figure 1.
Overview of somatic point mutation detection using MuTect.
MuTect takes as input tumor (T) and normal (N) next generation sequencing data and, after removing low quality reads (Supplementary Methods), determines if there is evidence for a variant beyond the expected random sequencing errors. Candidate variant sites are then passed through six filters to remove artifacts (Table 1). Next, a Panel of Normals is used to screen out remaining false positives caused by rare error modes only detectable in additional samples. Finally, the somatic or germline status of passing variants is determined using the matched normal.