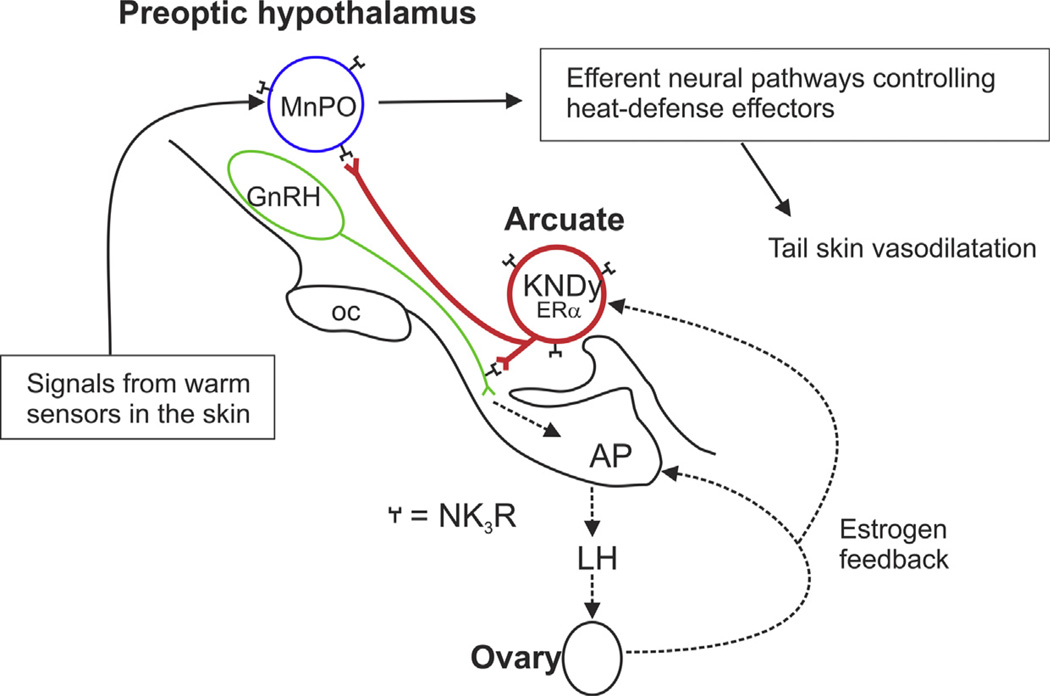
Fig. 9.
Schematic diagram showing the relationship between KNDy neurons, GnRH neurons and the heat-defense pathway in the rat. KNDy neurons branch and project to GnRH terminals in the median eminence and preoptic structures that regulate body temperature (Krajewski et al., 2005, 2010; Nakamura and Morrison, 2010; Romanovsky et al., 2009; Tanaka et al., 2009; Yeo and Herbison, 2011; Yoshida et al., 2009). Secretion of GnRH into portal capillaries stimulates LH secretion from the anterior pituitary gland, which stimulates the secretion of estrogen (E2) from the ovaries. E2 negative feedback reduces serum LH and decreases NKB and kisspeptin mRNA in KNDy neurons (Rance and Bruce, 1994; Smith et al., 2005a). ERa, the isoform required for estrogen negative feedback (Dorling et al., 2003), is expressed in arcuate KNDy neurons (Burke et al., 2006) but not GnRH neurons (Hrabovszky et al., 2001). NK3R is expressed on arcuate KNDy neurons (Burke et al., 2006) and GnRH terminals in the median eminence (Krajewski et al., 2005). GnRH neurons express kisspeptin receptor mRNA (Han et al., 2005), but the location of the kisspeptin receptor protein on GnRH neurons has not been described. MnPO neurons express NK3R. The MnPO receives information from warm-sensitive, cutaneous thermoreceptors and project to CNS structures to modulate heat-dissipation effectors (Nakamura and Morrison, 2010; Yoshida et al., 2009). Not shown are KNDy neuron projections to the medial preoptic area, which contains warm-sensitive GABAergic neurons which may also express NK3R (Eberwine and Bartfai, 2011). Modified with permission from (Mittelman-Smith et al., 2012a).