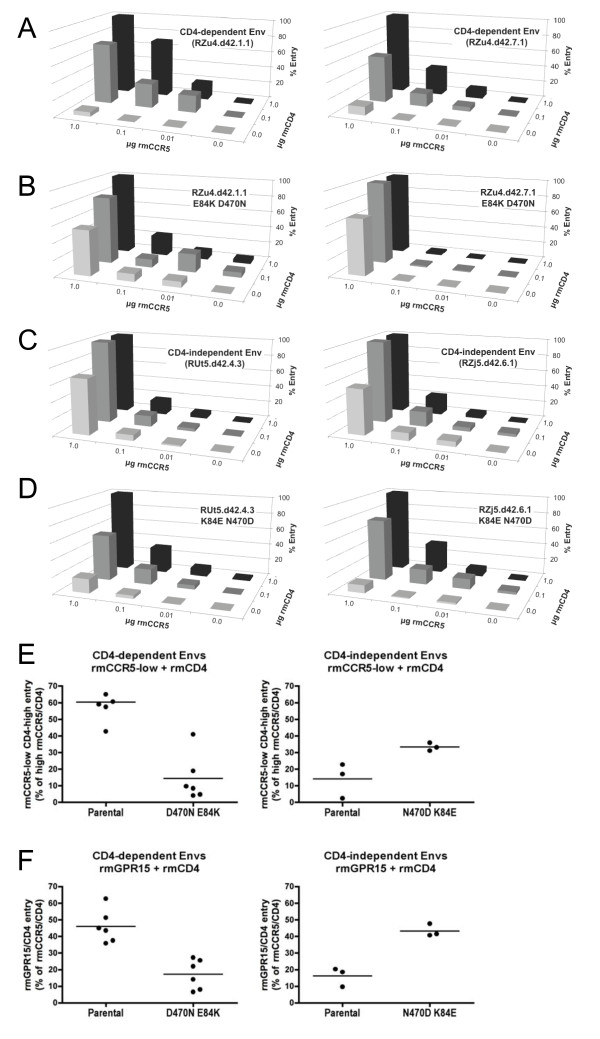
Figure 5.
Env D470N and E84K determine efficiency of CCR5 and GPR15 use. Mutations that emerged in vivo which conferred CD4 independence (D470N and E84K) were introduced into CD4-dependent Envs, and mutations that abrogate CD4 independence (N470D and K84E) were introduced into CD4-independent Envs. (A-D) Two representative parental CD4-dependent Envs (A) and their respective mutated forms (B) and two representative parental CD-independent Envs (C) and their respective mutated forms (D), were assessed for their ability to mediate entry into cells transfected with varying amounts of rmCCR5 and rmCD4, as described in Figure 2. (E) Use of low rmCCR5 levels by all parental and mutant Envs (10% maximal CCR5 in the presence of maximal CD4), with each Env indicated as a dot and entry in the presence of maximal CCR5/CD4 set at 100%. (F) Use of GPR15 by parental and mutated Envs were tested based on entry into cells transfected with rmGPR15 and rmCD4, with each Env indicated as a dot and expressed as a percentage of entry in the presence of rmCCR5/rmCD4.