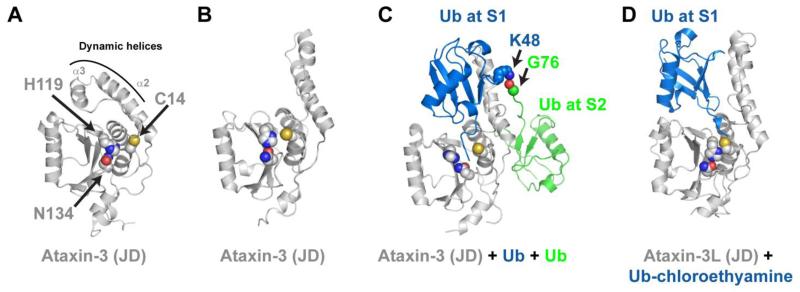
Figure 3.
The Josephin domain (JD) contains multiple ubiquitin binding sites. (A) NMR solution structure of the Ataxin-3 Josephin domain with residues of the catalytic triad shown as spheres (PDB 2AGA). (B) An adopt an alternative conformation (PDB 1YZB). (C) Solution structure of Ataxin-3 JD non-covalently associated with two ubiquitin molecules (PDB 2JRI). One ubiquitin is bound at the S1 site and its C-terminal tail bisects the catalytic Cys-His pair, possibly a reflection of the product complex that follows hydrolysis of the isopeptide bond. A second ubiquitin is bound at the S2 site of the Josephin domain, and its C-terminus is juxtaposed with K48 of ubiquitin bound at the S1 site. (D) Crystal structure of the Ataxin-3L JD covalently bound to Ub-chloroethylamine (PDB 3O65). This structure reveals the Ataxin-3L JD binds ubiquitin at the S1 site using different residues and positions ubiquitin in an alternate conformation.