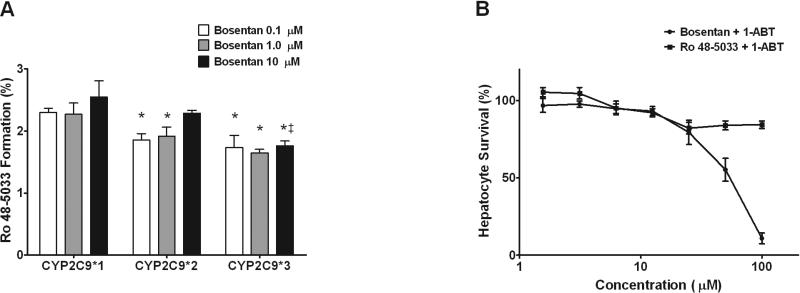
Figure 3.
Bosentan metabolism by CYP2C9 variant proteins and CYP-dependent hepatotoxicity. (A) rCYP2C9*1 (reference), rCYP2C9*2 and rCYP2C9*3 were incubated with 0.1, 1 and 10 μM bosentan for 0 and 60 min and formation of Ro 48-5033 was quantified by LC/MS/MS. Data are presented as percent of bosentan converted to Ro 48-5033 ± S.D. (N=3). *P < 0.05 for difference between CYP2C9 reference and variants; ‡P < 0.05 for difference between CYP2C9*2 and CYP2C9*3. (B) Hepatocytes pre-incubated with 1-aminobenzotriazle were treated with increasing concentrations (0 – 100 μM) of bosentan or its metabolite Ro 48-5033 for 48 hours. Cell viability was assessed by measuring cellular ATP and GSH levels. Data are presented as percent of vehicle control. IC50 values were calculated using GraphPad Prism software.