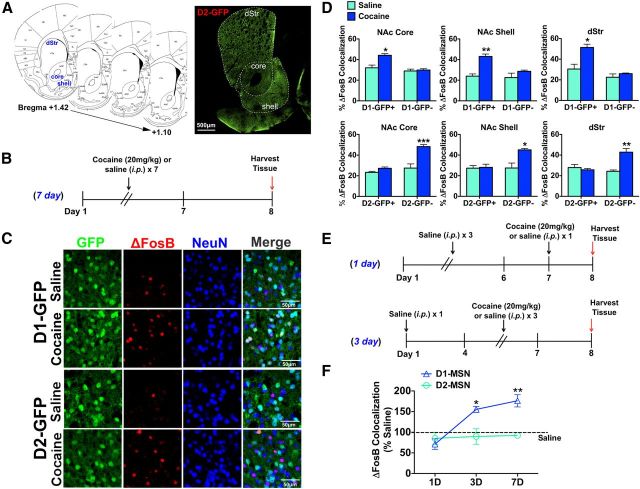
Figure 1.
Chronic cocaine selectively induces ΔFosB in D1-MSNs in striatal regions. A, Striatal sections from bregma +1.42 to + 1.10 were used for cell counting. Image of a D2-GFP striatal section demonstrates the three striatal regions studied: NAc core, NAc shell, and dStr. Scale bar, 500 μm. B, Time course of chronic (7 d) cocaine (20 mg/kg, i.p.) or saline treatment, with brains harvested 24 h after the last dose. C, Immunohistochemistry of NAc shell of D1-GFP and D2-GFP mice after chronic cocaine (20 mg/kg, i.p) or saline. Immunolabeling for GFP (green), ΔFosB (red), or NeuN (blue) shows induction of ΔFosB in GFP+/NeuN+ neurons in D1-GFP NAc shell or GFP−/NeuN+ neurons in D2-GFP NAc shell. Scale bar, 50 μm. D, Cocaine treatment significantly induces ΔFosB in GFP+/NeuN+ neurons (D1-MSNs) in D1-GFP mice but not in GFP−/NeuN+ neurons (D2-MSNs) in the same mouse. Two-way ANOVA, NAc core: drug × cell type F(1,12) = 16.41, p < 0.05, Bonferroni post test: *p < 0.01; NAc shell: drug × cell type F(1,12) = 12.41, p < 0.05, Bonferroni post test: **p < 0.001; dStr: drug × cell type F(1,12) = 12.07, p < 0.05, Bonferroni post test: *p < 0.01. A significant induction of ΔFosB by cocaine is also observed in GFP−/NeuN+ (D1-MSNs) but not GFP+/NeuN+ neurons (D2-MSNs) in D2-GFP mice. Two-way ANOVA, NAc core: drug × cell type F(1,12) = 15.76, p < 0.01, Bonferroni post test: ***p < 0.0001; NAc shell: drug × cell type: F(1,12) = 20.33, p < 0.05, Bonferroni post test: *p < 0.01; dStr: drug × cell type: F(1,12) = 35.96, p < 0.01, Bonferroni post test: **p < 0.001. E, Time course study of cocaine induction of ΔFosB in dStr. F, Cocaine significantly induces ΔFosB in D1-MSNs only after 3 or 7 d of cocaine exposure (two-way ANOVA, cell type × day F(2,13) = 17.87, p < 0.01, Bonferroni post test: *p < 0.01, **p < 0.001).