Figure 4.
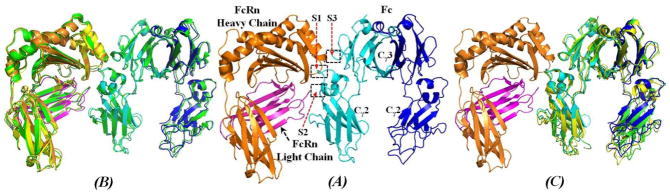
The energy-minimized structure of human FcRn-Fc binding complex in comparison with reported X-ray crystal structures of lignd-free human FcRn and human Fc. (A) The heavy chain of human FcRn is represented as orange ribbon, and magenta ribbon for the light chain (β2m) of human FcRn. Human Fc is also represented as ribbon colored in cyan for one subunit and blue for another subunit. The binding interface between human FcRn and human Fc is roughly represented as three subsites (S1, S2, and S3) as labeled. (B) Human FcRn-Fc complex superimposed with that of rat FcRn-Fc complex26 (PDB code 1I1A, green ribbon), ligand-free human FcRn22 (PDB code 3M17, yellow ribbon); only Cα atoms were used in the superimposition. The positional RMSD for Cα atoms between human FcRn-Fc structure and the rat FcRn-Fc structure is 0.96 Å, and the RMSD between the human FcRn in human FcRn-Fc complex and the ligand-free human FcRn is 0.79 Å. (C) Human FcRn-Fc binding complex superimposed with two typical ligand-free Fc structures. One ligand-free human Fc structure corresponding to PDB code 3AVE28 (green ribbon) has a positional RMSD value of 1.55 Å for the Cα atoms. Another ligand-free human Fc structure corresponding to PDB code 1H3Y27 (yellow ribbon) has an RMSD value of 1.85 Å. Obvious differences appeared at the relative position of the Cγ2 domain of each subunit of human Fc dimer.
