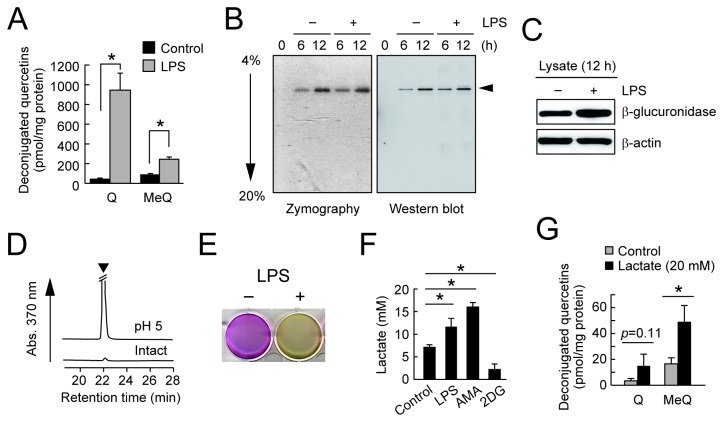
Figure 3. β-Glucuronidase activity in LPS-treated RAW264 cells.
(A) Enhanced deconjugation of Q3GA in the LPS-stimulated RAW264 cells. Cells were pretreated with LPS (1 μg/ml) for 8 h followed by treatment with Q3GA (20 μM) for 1 h. The deconjugated quercetin derivatives, quercetin (Q) and methyquercetins (MeQ), in cells were analyzed by HPLC-ECD. (B) Zymography (left) and immunoblot (right, anti-β-glucuronidase) analysis of the cultured medium of RAW264 cells. Culture medium was collected at each time point after treatment with or without LPS. (C) Immunoblot analysis of the lysates of RAW264 cells treated with or without LPS for 12 h. (D) Acidification is required for the medium β-glucuronidase activity during culturing the RAW264 cells. The β-glucuronidase activity of the cultured medium (for 8 h) at pH 5.0 or intact was determined using Q3GA as a substrate. The arrow head in the HPLC profiles (monitored at 370 nm) shows the peaks for the quercetin aglycone. (E) Acidification of the medium upon LPS treatment. The picture shows the culture plate after treatment of the RAW264 cells with (right) or without (left) treatment with LPS for 24 h. Acidification turns the medium yellow. (F) Medium lactate levels during culturing RAW264 cells in the presence of LPS, antimycin-A (AMA, 5 μg/ml), or 2-deoxyglucose (2DG, 20 mM) for 6 h determined by LC-MS/MS analysis. Blocking of glycolysis by 2DG strongly inhibited the lactate secretion. (G) Effect of lactate supplementation in the medium on the deconjugation of Q3GA. Cells were treated with Q3GA in the absence or presence of lactate (20 mM) for 4 h. Data in all bar graphs are presented as the average ± S.D. (n=3). Asterisks indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05). NS, not statistically significant.