Figure 5.
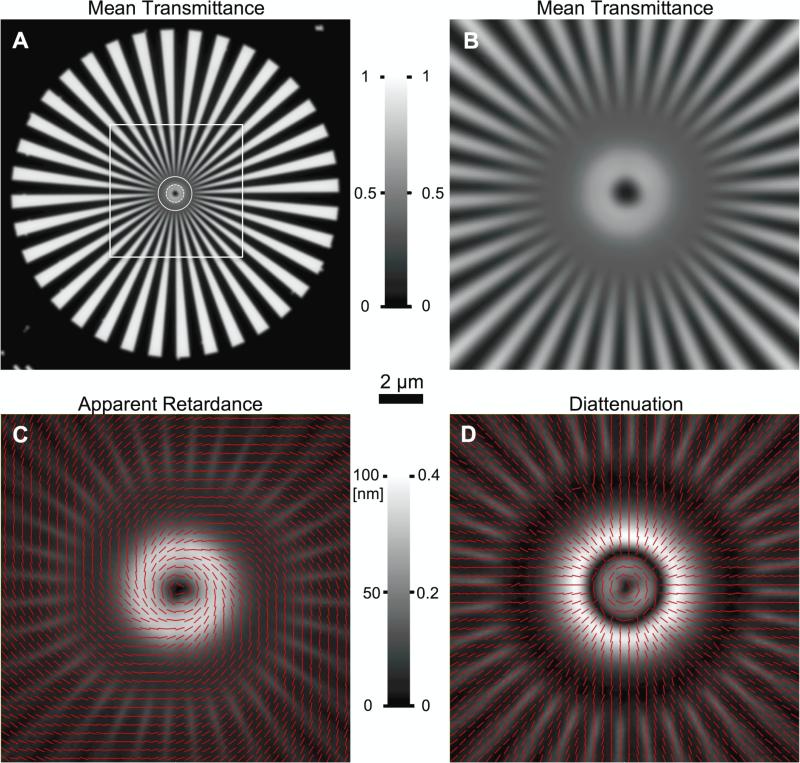
LC-PolScope images of a Siemens star etched into a 50 nm thick aluminum film on cover glass using electron lithography. The cover glass with film was mounted on a microscope slide using Permount. A Average transmittance of the star pattern, which consists of 36 wedge pairs and has an outside diameter of 75 μm. Near the outer edge along the circumference the grating period is 6.5 μm, which decreases continuously towards the smallest period of 0.1 μm near the inner black disk (dia. 1.2 μm). Near the white dashed circle, the period is 0.5 λ, and λ near the solid circle, with λ the wavelength of the illuminating light (630 nm). The square outlines the magnified portion in panels B to D. B to D Central portion of the Siemens star imaged with the LC-PolScope in different imaging modes: B Mean transmittance. Gray scale legend between panels A and B indicates mean transmittance and applies to both panels. C Apparent retardance of the central pattern with red lines indicating the slow axis orientation. D Diattenuation of the central pattern with red lines indicating the orientation of the maximum transmittance. In panels C and D lines are drawn for every 3rd pixel of the original image. Gray scale legend between panels C and D shows retardance scale for left and anisotropy scale for right panel. Scale bar in central part of the Figure applies for images in panels B to D.