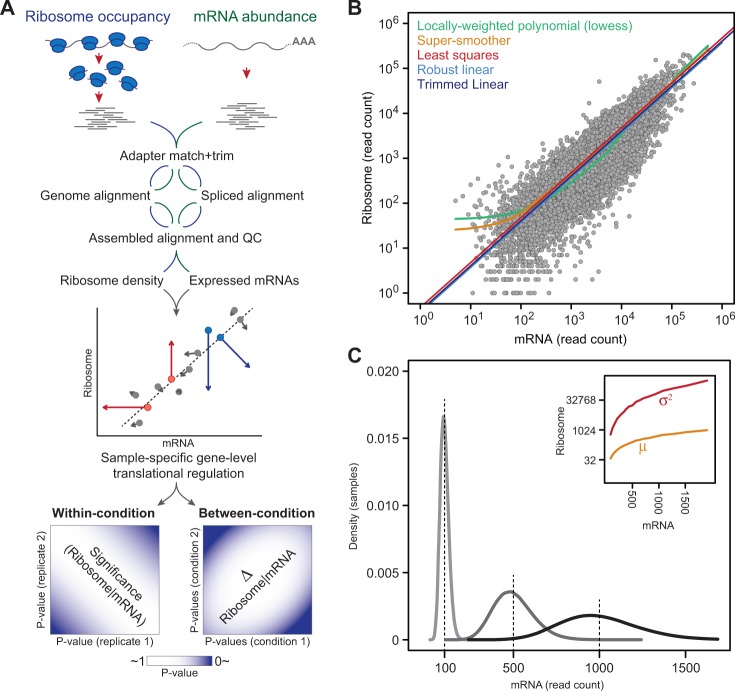
Fig. 1.
The Babel framework and analysis. (A) A schematic of the Babel framework in which ribosome profiling data are processed and aligned, and an NB-regression-NB model is developed in each sample to identify genes whose ribosome association is higher or lower (red and blue arrows, respectively) than expected (gray) from its mRNA expression level. Significant translationally regulated genes across all the samples of a given condition are determined (left) as are those that change significantly between conditions (right). (B) Although multiple candidate parametric and non-parametric regression forms were evaluated for estimating ribosome association based on mRNA abundance (plotted here as read counts in log-scale), the trimmed least squares approach was chosen (see text). (C) Errors-in-variables regression is justified by the intrinsic uncertainty of mRNA levels under the NB distribution where variability increases with increasing level of expression, demonstrated here for three genes with NB means of 100, 500 and 1000. The NB model of ribosome-given-mRNA counts is further necessitated by significantly greater variance than mean RPF counts across the distribution of mRNA abundance (inset)