Figure 10.
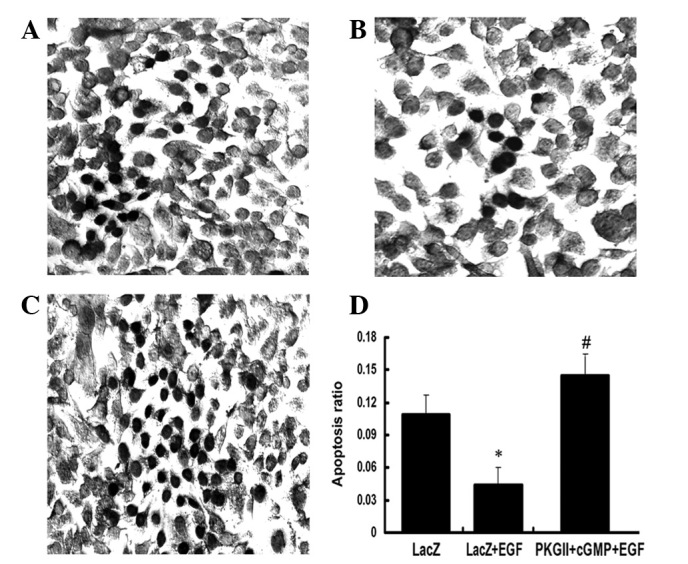
PKG II reverses the anti-apoptotic effect of EGF. The AGS cells were treated as in Fig. 5 and TUNEL staining was performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions of the In Situ Cell Death Detection kit. The cells with dark brown nuclear staining were considered to be apoptotic and were counted as described in Materials and methods. (A–C) Representatives of the staining. (A) The cells were infected with Ad-LacZ only. (B) The cells were infected with Ad-LacZ and incubated with 100 ng/ml EGF for 12 h. (C) The cells were infected with Ad-PKG II, incubated with 250 μM 8-pCPT-cGMP for 1 h and incubated with 100 ng/ml EGF for 12 h. (D) The average ratio of apoptotic cells per field (magnification, ×200) of each group (*P<0.05, compared with the LacZ group and #P<0.05, compared with the LacZ+EGF group). The results revealed that EGF treatment decreased the apoptosis of the AGS cells, while pre-infecting with Ad-PKG II and pre-incubating with 250 μM 8-pCPT-cGMP efficiently reversed the effect of EGF. PKG II, cGMP-dependent protein kinase Type II; EGF, epidermal growth factor; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end-labeling.
