Fig. 1.
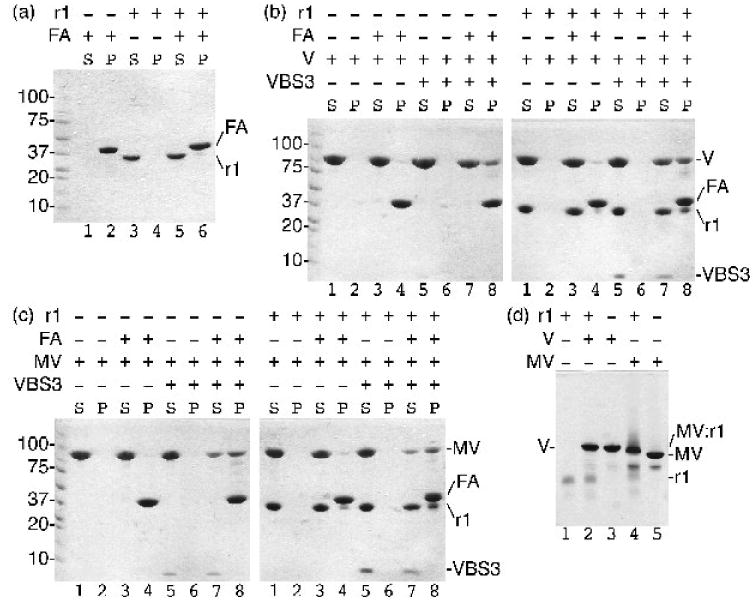
Raver1 binds to inactive metavinculin but not to inactive vinculin. Actin co-sedimentation assays as analyzed on a 8-25% gradient SDS PAGE gel established that:
(a) raver1 (residues 39-321) does not bind to F-actin (FA; raver1, r1, remains in the supernatant, S, while F-actin pellets, P); (b) raver1 binding is not sufficient to activate the latent F-actin binding properties of vinculin (left gel: vinculin, V, remains in the supernatant, lanes 1-2; inactive vinculin does not bind to F-actin, FA, lanes 3-4; vinculin activated by talin VBS3, VBS3, remains in the supernatant, lanes 5-6; the vinculin:VBS3 complex binds to F-actin, lanes 7-8. Right gel: vinculin and raver1, r1, are soluble, lanes 1-2; vinculin and raver1 do not bind to F-actin, lanes 3-4; vinculin, raver1, and VBS3 remain soluble, lanes 5-6; vinculin activated by VBS3 pellets with F-actin, lanes 7-8); and (c) raver1 binding is not sufficient to activate the latent F-actin binding properties of metavinculin (left gel: metavinculin, MV, remains in the supernatant, lanes 1-2; inactive MV does not bind to F-actin, lanes 3-4; MV activated by VBS3 remains in the supernatant, lanes 5-6; the MV:VBS3 complex binds to F-actin, lanes 7-8. Right gel: MV and raver1 are soluble, lanes 1-2; MV and raver1 do not bind to F-actin, lanes 3-4; MV, raver1, and VBS3 remain soluble, lanes 5-6; MV activated by VBS3 pellets with F-actin, lanes 7-8)
(d) Native gel shift mobility assay of raver1 alone (lane 1), vinculin, V, alone (lane3), metavinculin, MV, alone (lane 5), vinculin incubated with raver1 (lane 2), and metavinculin incubated with raver1 (lane 4) shows that a new band is formed corresponding to MV:raver1 complex formation under physiological conditions without pre-activation of MV by a VBS. In contrast, no vinculin:raver1 complex is formed (lane 2).
