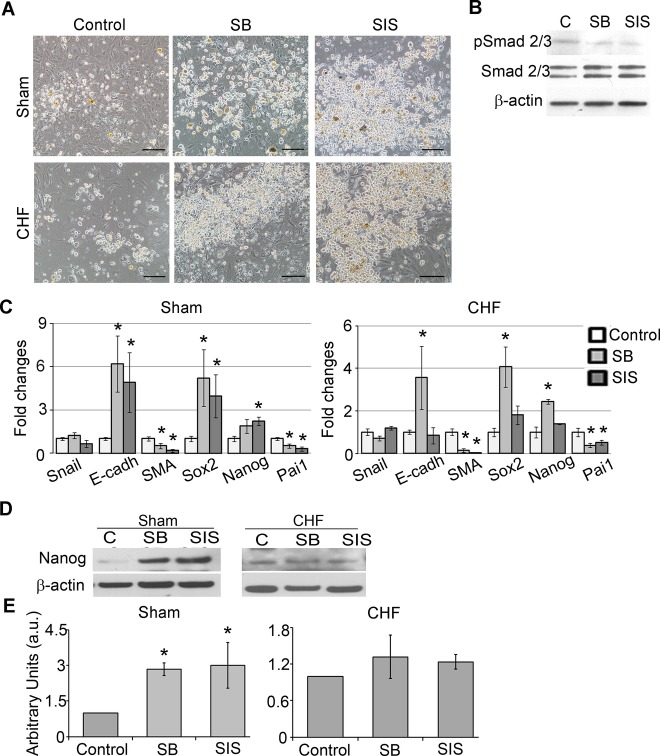
Figure 3.
TGF‐β inhibition suppressed EMT and upregulated pluripotency gene expression in c‐Kit+ cells. TGF‐β signaling was inhibited by suppression of TGF‐β receptor type 1 (SB) or by suppression of Smad2/3 phosphorylation (SIS) for 7 days. A, SB and SIS treatments increased amounts of round phase‐bright cells compared with control. Scale bar=100 μm. B, Western blot analysis of c‐Kit+ cells treated with SB and SIS showed reductions of pSmad2/3 levels. C, qRT‐PCR analysis of EMT‐ and pluripotency‐related gene expression in SB‐ and SIS‐treated c‐Kit+ cells from sham and CHF explants. Fold changes were calculated as a ratio of the expression in the SB‐ or SIS‐treated group to the expression in the control group. n=5 per condition. *Fold changes >2. D, Western blot analysis of Nanog in SB‐ and SIS‐treated c‐Kit+ cells. β‐Actin was used as a loading control. Representative blots are shown. E, Densitometry analysis of Nanog. n=3 per condition. *P<0.05, inhibitor‐treated cells vs untreated control. CHF indicates chronic heart failure; EMT, epithelial to mesenchymal transition; qRT‐PCR, quantitative reverse‐transcription polymerase chain reaction; SMA, α‐smooth muscle actin; TGF‐β, transforming growth factor–β.