Figure 8.
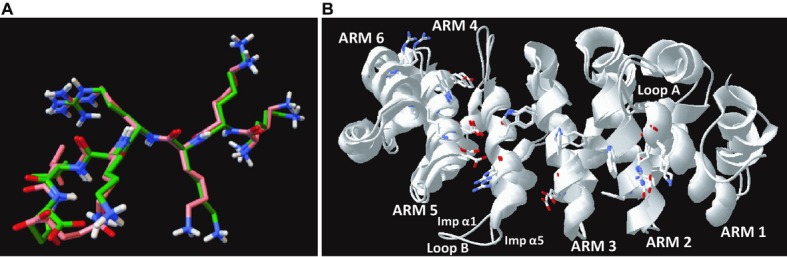
Three‐dimensional models. A, Unaligned images of the conformation of SV40 NLS obtained from the control modeling of its interaction with mouse Imp α1 (orange) and the structure of the same NLS motif obtained from x‐ray Crystallography (PDB ID: 1Q1SChain B) (green) are shown overlapped. Functional atoms are color coded: red, oxygen; blue, nitrogen; white, polar hydrogen. The RMSD of α carbons and all backbone atoms of unaligned conformations equals 0.58 and 0.77 Å, respectively. When aligned, the RMSD of α carbons and all backbone atoms equals 0.36 and 0.56 Å, respectively. Conformation of SV40 NLS were generated by AutoDock Vina 1.1.2 and visualized in PythonModelViewer 1.5.6. B, Imp α1 and α5 structures display high homology. Superimposed ribbon structures of the major NLS binding pockets from human Imp α1 (KPNA2, PDB ID: 3FEY Chain C) and human Imp α5 (KPNA1, PDB ID: 3TJ3 Chain B). The positions of structural components, including the major functional residues on the surface of NLS binding pockets, indicate a high degree of structure and sequence similarity. Loop B was identified as a region of structural diversity, in addition to IADR‐1 and IADR‐2 (see Figure 2). Structures were visualized in DeepView software (Swiss‐PdbViewer 4.1.0, Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics, http://spdbv.vital-it.ch/). ARM indicates armadillo; IADR, importin α diversity region; Imp α, importin α; NLS, nuclear localization sequence; RMSD, root mean square deviation.
