Figure 4.
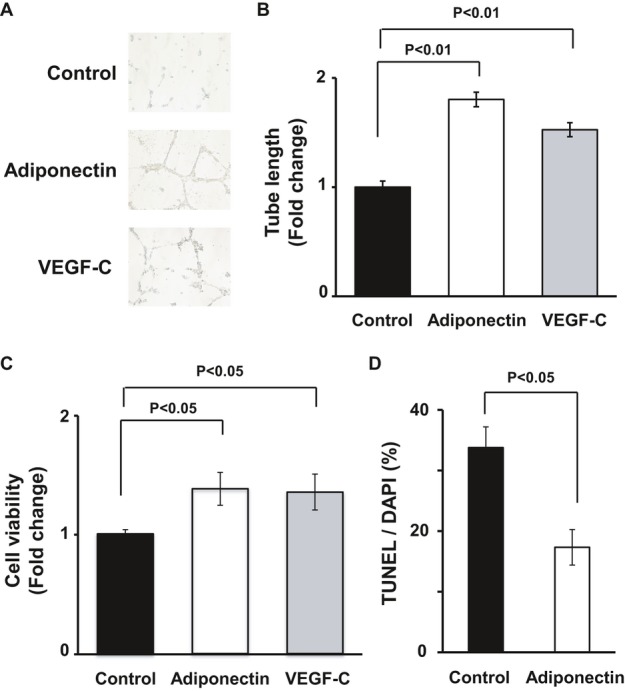
Adiponectin promotes lymphatic endothelial cell differentiation and survival in vitro. A and B, Representative photomicrographs of network formation of LECs (A) and quantitative analyses of network tube length (B) (n=3 in each group). After 18 hours of serum deprivation, LECs were cultured in Matrigel‐coated dishes in the presence of recombinant adiponectin protein (30 μg/mL), VEGF‐C (50 ng/mL), or vehicle. C, WST‐1–based assay for evaluating cell viability was performed. LECs were treated with adiponectin (30 μg/mL), VEGF‐C (50 ng/mL), or vehicle in serum‐starved media for 48 hours (n=4 in each group). Results are expressed relative to the values compared with control. D, TUNEL assay for detecting apoptotic cells was performed. LECs were treated with adiponectin (30 μg/mL) or vehicle in serum‐starved media for 48 hours (n=5 in each group). Results are shown as the mean±SE. DAPI indicates 4′,6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole; LEC, lymphatic endothelial cell; TUNEL, transferase–mediated dUTP nick‐end labeling.
