Figure 2. Aβ42 levels in the CSF decrease while tot-tau and p-tau levels increase with respect to disease progression in AD temporal cortex.
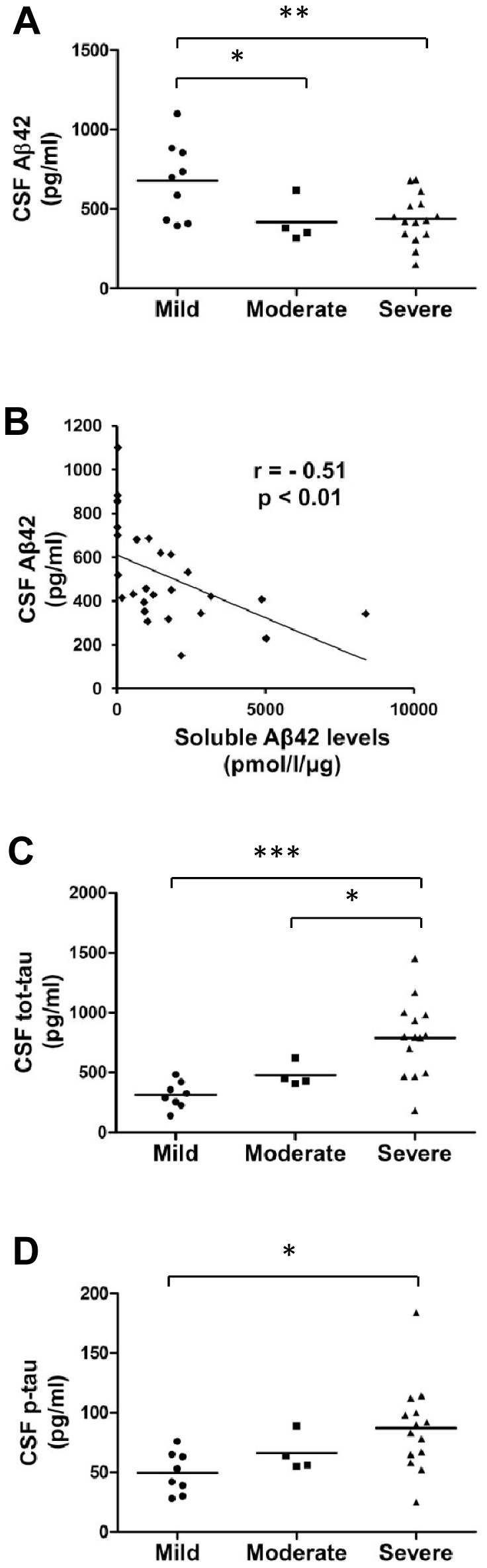
(A) CSF Aβ42 levels are significantly decreased in both moderate and severe groups as compared to the mild group (**p<0.01, *p<0.05, ANOVA, LSD, mild n = 9; moderate n = 4; severe n = 15). (B) CSF Aβ42 levels and soluble Aβ42 levels indicate a significant negative correlation in the temporal cortex samples (p<0.01, Pearson two-tailed correlation, n = 26). (C) CSF tot-tau levels are significantly increased in the severe group as compared to the mild and moderate groups (***p<0.001, *p<0.05, ANOVA, LSD, mild n = 8; moderate n = 4; severe n = 14). (D) The p-tau levels in the CSF are significantly increased in the severe group as compared to the mild group (*p<0.05, ANOVA, LSD, mild n = 8; moderate n = 4; severe n = 14). Mean values are indicated in the graphs and each dot represents one individual.
