Figure 6.
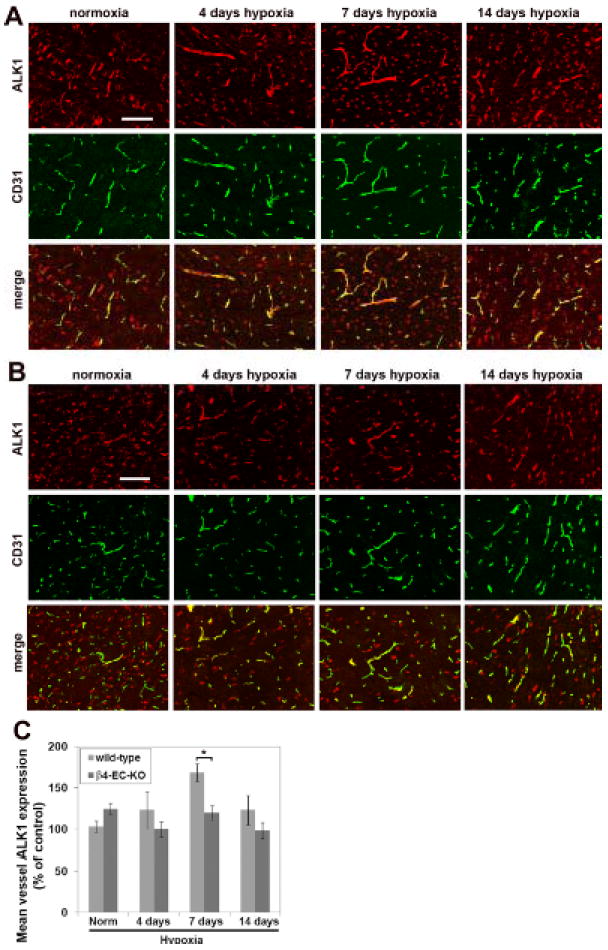
Comparison of hypoxic-induced endothelial expression of ALK1 in the brains of wild-type and β4-EC-KO mice. Wild-type litter-mate (A) and β4-EC-KO (B) mice were maintained at normoxia or exposed to mild hypoxia (8% O2) for 4, 7 or 14 days before frozen sections of brainstem were subject to CD31/ALK1 dual-IF. Scale bar = 100μm. C. Quantification of endothelial ALK1 expression. The fluorescent intensity of vessels was measured using the Volocity software program and the results presented as mean vessel ALK1 expression (% of control level in normoxic wild-type mice). Results represent mean ± SEM of four different mice per condition. Note that while hypoxia induced a significant increase in endothelial ALK1 expression in wild-type mice, β4-EC-KO mice failed to show this response. * P< 0.05.
