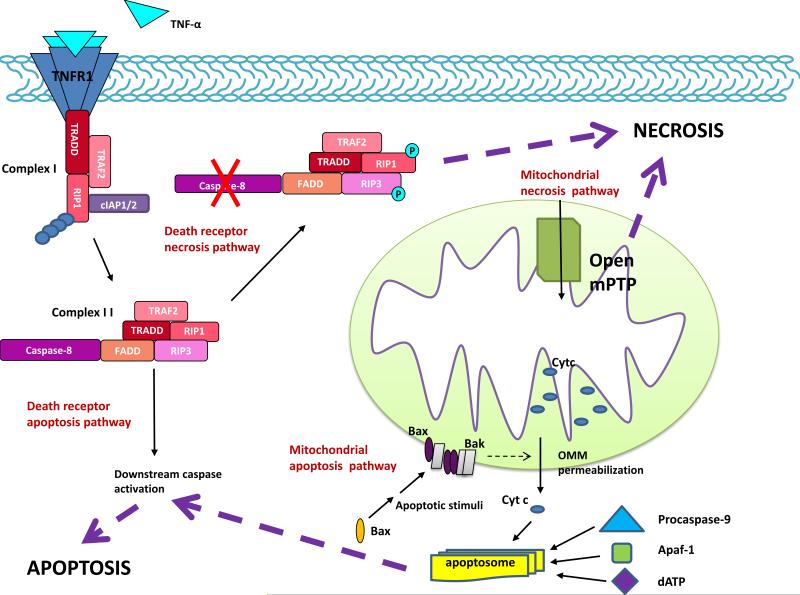
Figure. Cell death pathways.
Apoptosis and necrosis are mediated by death receptor (extrinsic) and mitochondrial (intrinsic) pathways. In the death receptor pathway, a death ligand (e.g. TNF-α) binds its cognate death receptor to trigger assembly of either the DISC (not shown) or complex I. When RIP1 is K63-polyubiquinated by cIAP1/2, complex I signals survival through NF-kB activation (not shown). If (a) death receptor dissociates from complex I, (b) the complex is endocytosed, (c) RIP1 undergoes deubiquitiniation, and (d) a FADD-RIP3 complex is recruited, complex II is formed. This complex signals apoptosis or necrosis depending on procaspase-8 activity. Activation of procaspases-8 leads to cleavage and activation of downstream procaspases that proteolyze cellular proteins to bring about apoptosis. Procaspase-8 also cleaves RIP1 and RIP3, to preclude necrosis. In contrast, with caspase-8 inhibition, RIP1 and RIP3 undergo a series of cross-phosphorylation events that trigger necrosis by a variety of mechanisms (see text). In the mitochondrial pathway, the critical event in apoptosis is permeabilization of the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM), which results in release of mitochondrial apoptogens (e.g. cytochrome c) to the cytoplasm. Complex interactions among Bcl-2 family members (e.g. Bax and Bak) mediate OMM permeabilization (see text). Once in the cytoplasm, cytochrome c stimulates assembly of the apoptosome, a multiprotein complex in which procaspase-9 is activated. Procaspase-9 goes on to activate downstream procaspases. In contrast, the defining event in necrosis is opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) in the inner membrane, which (a) collapses the electrical gradient across the IMM leading to cessation of ATP synthesis and (b) promotes the influx of water into the mitochondrial matrix resulting in severe mitochondrial swelling. Multiple connections exist between these pathways. TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor α, TNFR1, tumor necrosis factor receptor 1, RIP1, receptor interacting protein 1, cIAP1/2, cellular inhibitor of apoptosis 1 and 2, FADD, Fas-associated via death domain, RIP3, receptor interacting protein 3, TRADD, TNF receptor-associated death domain, TRAF2, TNFR-associated factor 2, Cyt c, cytochrome c, Bax, Bcl-2 associated X protein, Bak, Bcl-2 homologous antagonist/killer, Apaf-1, apoptotic protease activating factor-1.