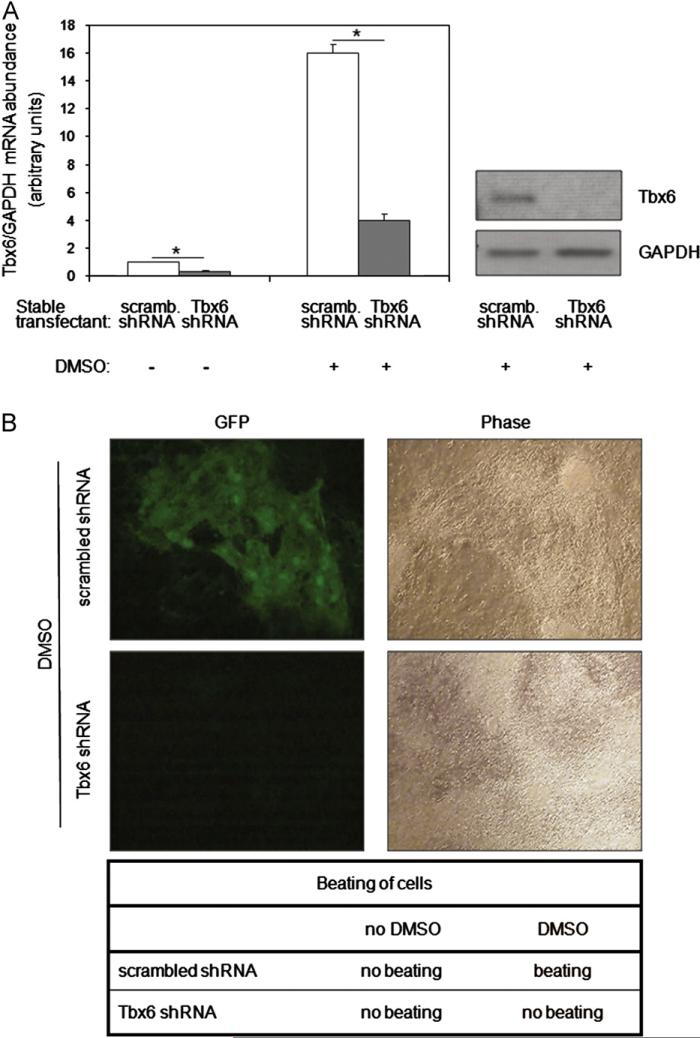
Fig. 3.
Tbx6 is essential for DMSO-induced cardiac myocyte differentiation. (A) Knockdown of basal and DMSO-induced levels of Tbx6 in P19CL6-MLC-2v-GFP cells. Scrambled (scramb) shRNA or Tbx6 shRNA stable transfectants were cultured with or without DMSO for 6 days. Levels of Tbx6 and GAPDH mRNA were assessed by qRTPCR, and the abundance of Tbx6 mRNA normalized to that of GAPDH mRNA (displayed in left panel as mean ± SD). *P < 0.01 for Tbx6 shRNA vs. scrambled shRNA. Tbx6 protein levels were assessed at the same time point by Western blot (right panel). Results are the representative of three independent experiments. (B) Tbx6 knockdown ablates MLC-2v promoter activity and spontaneous beating. Scrambled shRNA and Tbx6 shRNA stable transfectants were cultured with DMSO for 17 days following which the expression of MLC-2v-driven GFP was assessed by fluorescence microscopy. The presence or absence of beating is indicated below the figure (also see movies in Supplementary information). The onset of beating in scrambled shRNA with DMSO treatment was detected at day 10. Similar results were obtained in the four independent experiments.