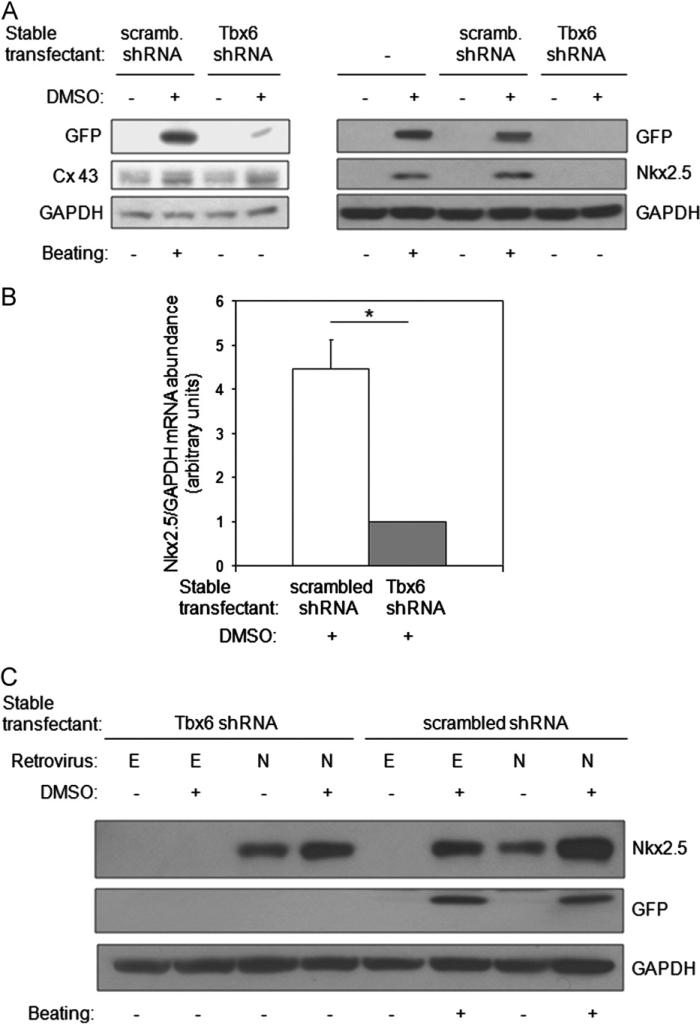
Fig. 4.
Tbx6 is necessary for the activation of Nkx2.5 expression during DMSO-induced cardiac myocyte differentiation. (A) Tbx6 knockdown decreases protein levels of Nkx2.5, but not Connexin43 (Cx43). Untransfected P19CL6-MLC-2v-GFP cells or cells stably expressing scrambled shRNA or Tbx6 shRNA were cultured with or without DMSO for 10 days. The abundance of the indicated proteins was assessed by Western blot and spontaneous beating by direct observation. Results are the representative of three independent experiments. (B) Tbx6 knockdown decreases the induction of Nkx2.5 mRNA by DMSO. P19CL6-MLC-2v-GFP cells stably expressing scrambled shRNA or Tbx6shRNA were treated with or without DMSO for 4 days and harvested at day 6. Nkx2.5 and GAPDH mRNA levels were assessed by qRT-PCR. Results are expressed as mean ± SD. Data are from three independent experiments. *P < 0.05. (C) Nkx2.5 overexpression fails to rescue defective cardiac myocyte differentiation resulting from Tbx6 knockdown. P19CL6-MLC-2v-GFP cells stably expressing Tbx6 shRNA or scrambled shRNA were cultured with or without DMSO for 4 days. Following this, they were infected with a retrovirus constitutively expressing Nkx2.5 (labeled N) or a retrovirus containing empty vector (labeled E). Cells were observed for the onset of beating and harvested at day 10. The abundance of the indicated proteins was assessed by Western blot. Data are the representative of three independent experiments.