Abstract
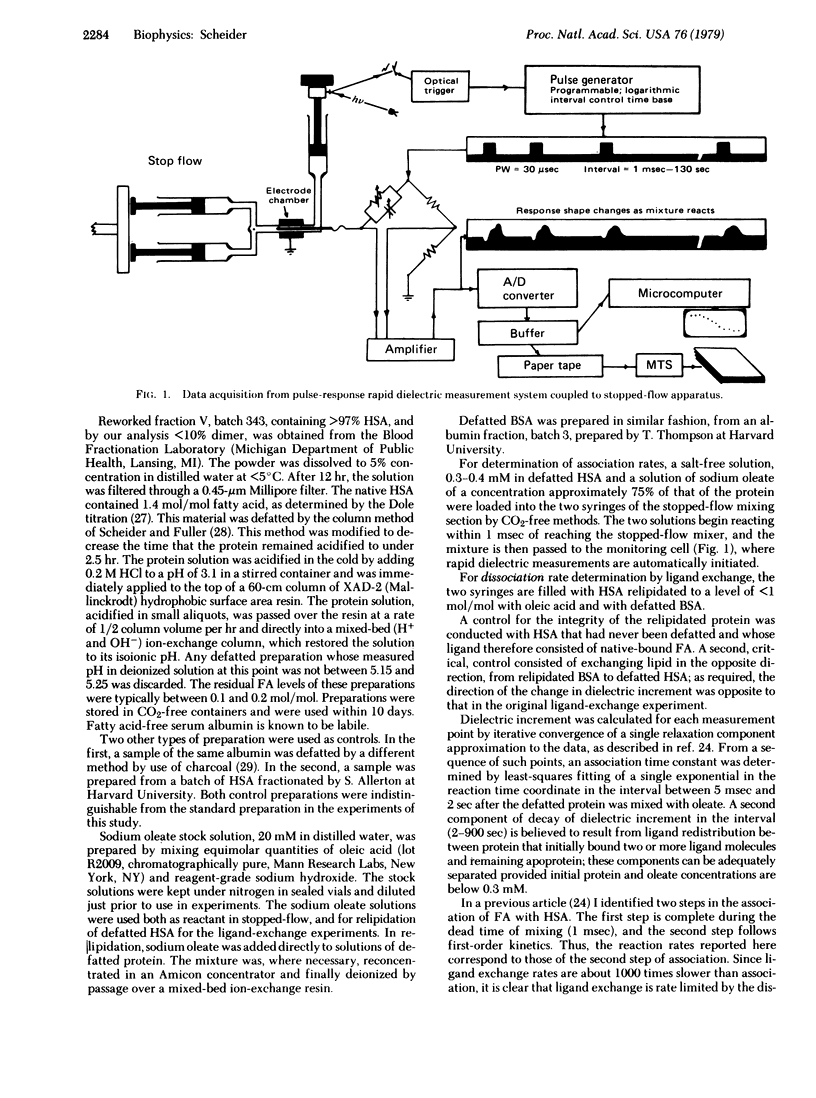
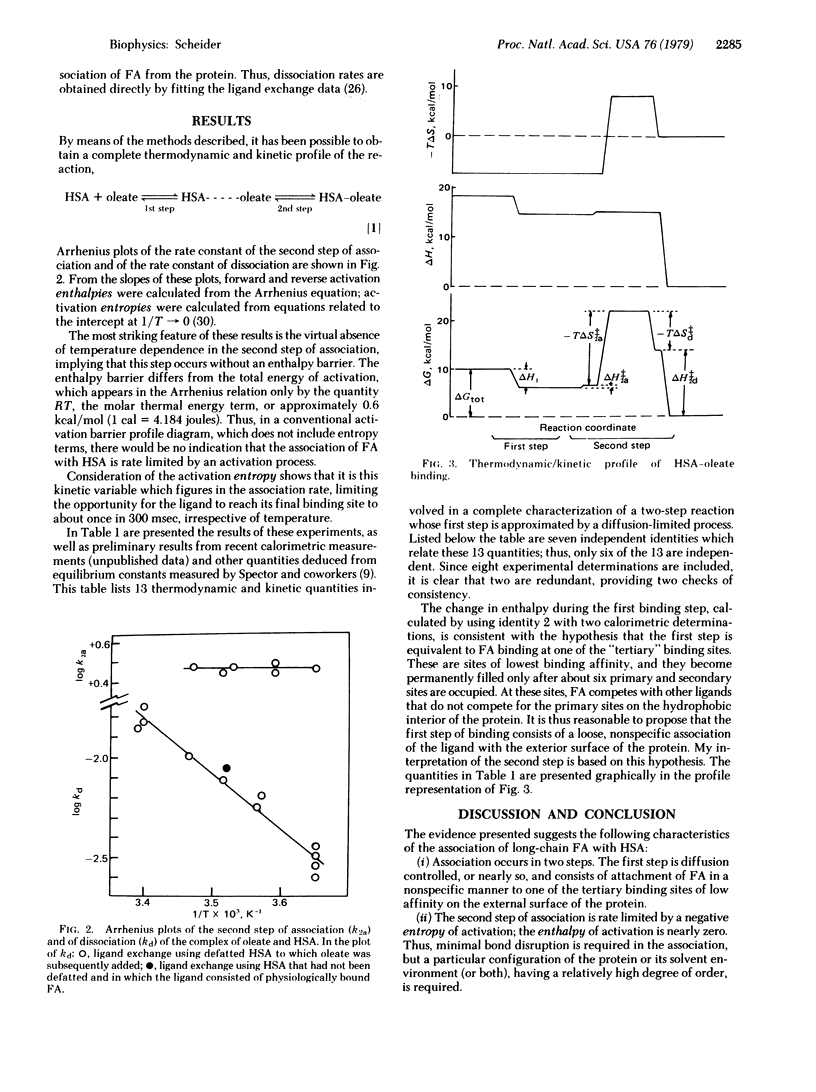
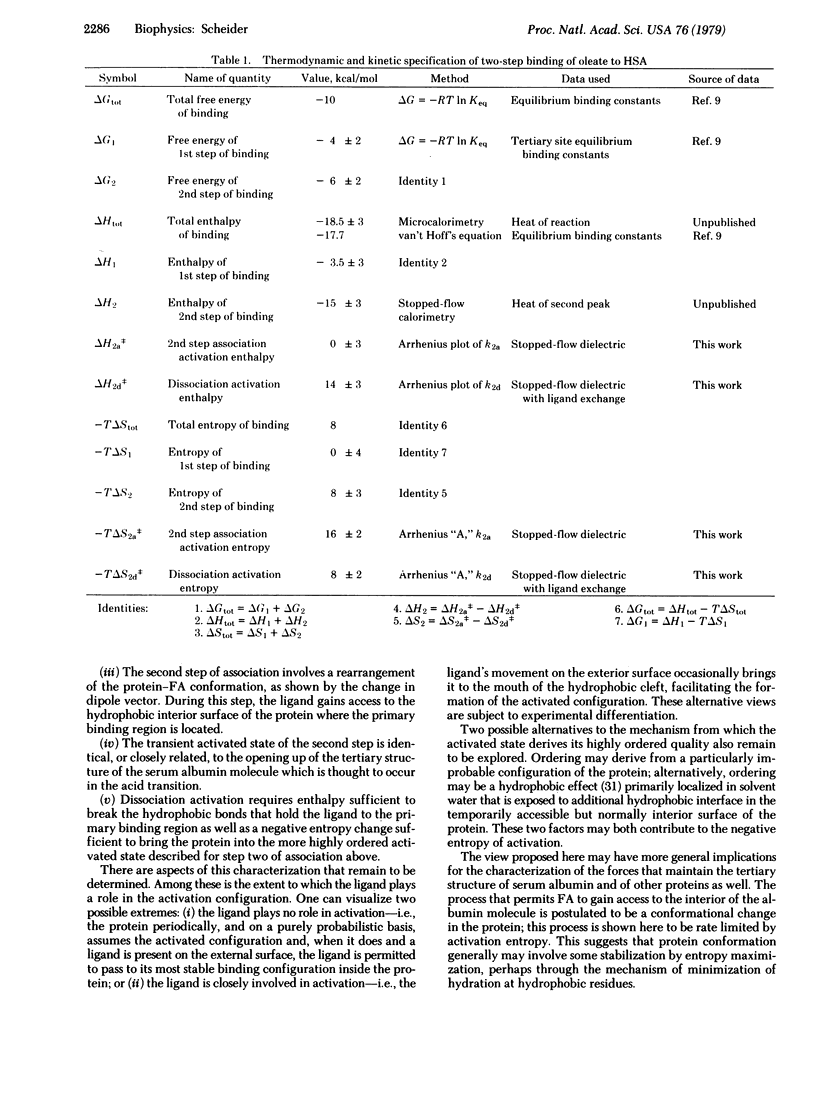
The technique of real time dielectric relaxation measurement coupled with a conventional stopped-flow device has made it possible to measure the rates of association and dissociation of the complex of human serum albumin with its most prevalent ligands, the long-chain fatty acids. This association was previously shown to proceed in two steps: a fast, probably diffusion-controlled, nonspecific association, followed by a slower (approximately 3 sec--1) rearrangement of the intermediate protein--ligand configuration, whose kinetics is first order. By use of the Arrhenius relation and standard theory of rate processes it is determined that there is virtually no activation enthalpy in the forward binding reaction and that the rate of access to the interior hydrophobic binding region of serum albumin is controlled by a negative entropy of activation, reflecting a high degree of ordering in the transition state. A complete thermodynamic and kinetic profile of the association reaction is given.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashbrook J. D., Spector A. A., Santos E. C., Fletcher J. E. Long chain fatty acid binding to human plasma albumin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 25;250(6):2333–2338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti S., Laliberté R., Brodeur J. Influence of long-chain free fatty acids on the binding of waraarin to bovine serum albumin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Nov 15;25(22):2515–2521. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90458-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. F. Fluorescence stopped-flow study of relaxation processes in the binding of bilirubin to serum albumins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jan;160(1):106–112. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(74)80014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. F. Removal of fatty acids from serum albumin by charcoal treatment. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jan 25;242(2):173–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLE V. P. A relation between non-esterified fatty acids in plasma and the metabolism of glucose. J Clin Invest. 1956 Feb;35(2):150–154. doi: 10.1172/JCI103259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOSTER J. F., SOGAMI M., PETERSEN H. A., LEONARD W. J., Jr THE MICROHETEROGENEITY OF PLASMA ALBUMINS. I. CRITICAL EVIDENCE FOR AND DESCRIPTION OF THE MICROHETEROGENEITY MODEL. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2495–2502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladenson J. H., Shyong J. C. Influence of fatty acids on the binding of calcium to human serum albumin. Clin Chim Acta. 1977 Mar 1;75(2):293–302. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(77)90200-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloun B., Morávek L., Kostka V. Complete amino acid sequence of human serum albumin. FEBS Lett. 1975 Oct 15;58(1):134–137. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80242-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERSEN H. A., FOSTER J. F. THE MICROHETEROGENEITY OF PLASMA ALBUMINS. II. PREPARATION AND SOLUBILITY PROPERTIES OF SUBFRACTIONS. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2503–2507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. G., Feldhoff R. C., Clute O. L., Peters T., Jr Fragments of bovine serum albumin produced by limited proteolysis. Conformation and ligand binding. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4578–4583. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheider W., Dintzis H. M., Oncley J. L. Changes in the electric dipole vector of human serum albumin due to complexing with fatty acids. Biophys J. 1976 May;16(5):417–431. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85698-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheider W. Dissociation rate of serum albumin-fatty acid complex from stop-flow dielectric study of ligand exchange. Biophys J. 1978 Oct;24(1):260–262. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85371-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheider W., Fuller J. K. An effective method for defatting albumin using resin columns. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 17;221(2):376–378. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90280-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheider W. Real-time measurement of dielectric relaxation of biomolecules: kinetics of a protein-ligand binding reaction. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1977 Dec 30;303:47–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1977.tb55918.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjödin T. Circular dichroism studies on the inhibiting effect of oleic acid on the binding of diazepam to human serum albumin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Nov 15;26(22):2157–2161. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90268-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar L. A., Hudson B. S., Simoni R. D. Conjugated polyene fatty acids as fluorescent probes: binding to bovine serum albumin. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 15;16(23):5100–5108. doi: 10.1021/bi00642a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector A. A. Fatty acid binding to plasma albumin. J Lipid Res. 1975 May;16(3):165–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector A. A., John K. M. Effects of free fatty acid on the fluorescence of bovine serum albumin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Sep 20;127(1):65–71. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90202-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector A. A., John K., Fletcher J. E. Binding of long-chain fatty acids to bovine serum albumin. J Lipid Res. 1969 Jan;10(1):56–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector A. A., Santos E. C., Ashbrook J. D., Fletcher J. E. Influence of free fatty acid concentration on drug binding to plasma albumin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Nov 26;226:247–258. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb20486.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svenson A., Holmer E., Andersson L. O. A new method for the measurement of dissociation rates for complexes between small ligands and proteins as applied to the palmitate and bilirubin complexes with serum albumin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 14;342(1):54–59. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90105-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallner J. J. Binding of drugs by albumin and plasma protein. J Pharm Sci. 1977 Apr;66(4):447–465. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600660402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilding G., Feldhoff R. C., Vesell E. S. Concentration-dependent effects of fatty acids on warfarin binding to albumin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1977 Jun 15;26(12):1143–1146. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(77)90058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


