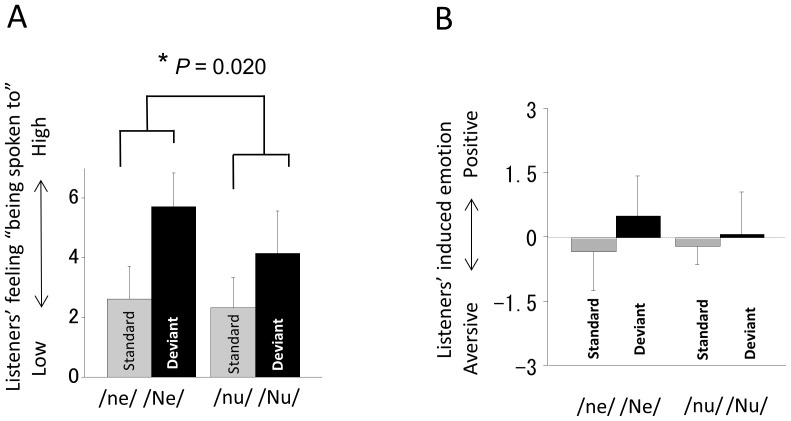
Figure 2. Differences in the intonational meaning of the standard/ne/and the deviant/Ne/or of the standard/nu/and the deviant/Nu/.
A, Ratings for listeners’ feelings of “being spoken to” following the standard/ne/or/nu/and the deviant/Ne/or/Nu/utterances; validation was by the subjects in the present study (n = 18). Repeated-measures ANOVA demonstrated a significant interaction between two factors (type of F0 contour×type of syllable; F = 6.61, * P = 0.020). The F0 contour effect of “ne” was stronger than that of “nu” for this kind of listeners’ feelings. B, Ratings for the emotion (aversive or comfortable) that listeners felt following the standard/ne/or/nu/and the deviant/Ne/or/Nu/utterances; validation is by the subjects in the present study (n = 18). There was no significant interaction between two factors (type of F0 contour×type of syllable; F = 2.59, P > 0.05), which means that the F0 contour effect of “ne” was not significantly different from that of “nu” for listener’s emotion. Error bars indicate 1 standard deviation.