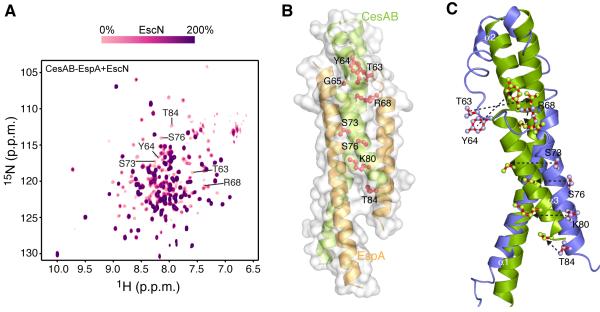
Figure 2. Interaction of CesAB–EspA with EscN.
(A) Overlaid 1H-15N HSQC spectra of the titration of U-2H-15N labeled CesAB–EspA with unlabeled hexameric EscN. Stepwise addition of EscN results in gradual resonance broadening of the interacting residues in CesAB–EspA. Spectra recorded at 10 different titration points are overlaid. The CesAB residues most affected by EscN binding are shown. The resonances not affected by EscN binding even at saturating concentrations of EscN are located in flexible regions of EspA that were crystallographically unresolved.
(B) CesAB–EspA residues (shown in red sticks) identified by NMR to be most affected upon binding to EscN. All these residues are located in helices α2 and α3 in CesAB.
(C) Superposition of the CesAB subunit of the homodimeric CesAB (blue) and the heterodimeric CesAB–EspA complex (green). The residues identified to mediate the binding to CesAB–EspA to EscN are shown.