Figure 4. Effect of murine ß-defensin 2 (Mbd2) on the frequency of NP-147 epitope-specific CD8+ T cells in the spleens of HAd-HA-NP vaccinated aged mice.
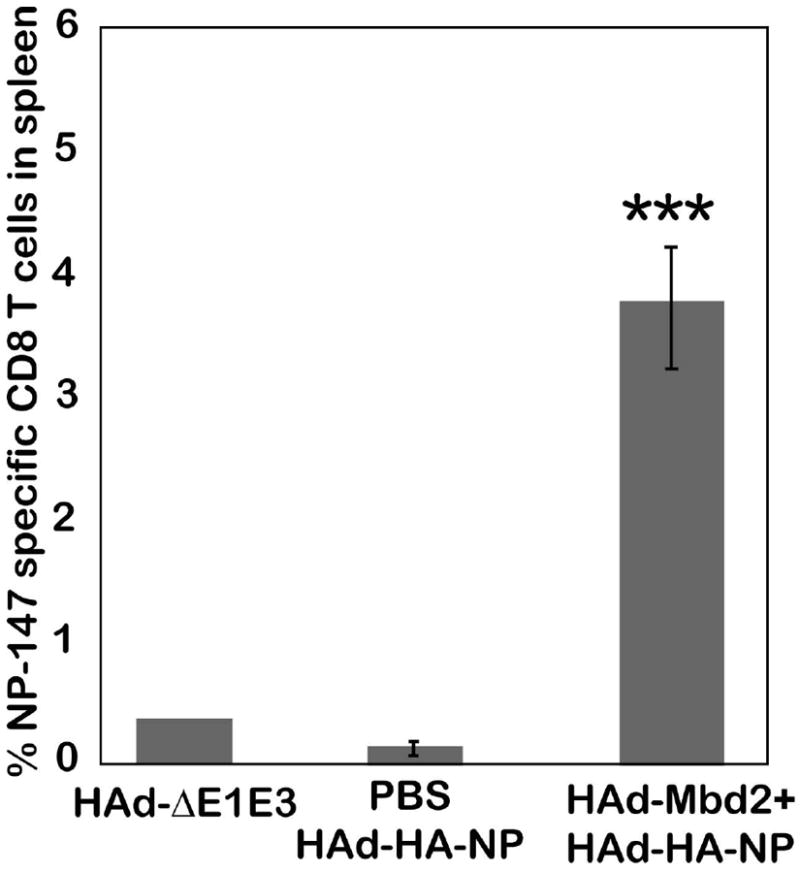
Aged mice (18 month-old) were inoculated intramuscularly (i.m.) either with phosphate-buffered saline or 1 ×108 plaque-forming units (pfu) of HAd-Mbd2 [adenovirus vector expressing murine ß-defensin 2 (Mbd2)]. Seven days later, animals were immunized with 1 × 108 pfu of HAd-HA-NP [adenovirus vector expressing hemagglutinin (HA) and nucleoprotein (NP) of a H5N1 influenza virus]. Animals similarly inoculated with 1 × 108 pfu of HAd-ΔE1E3 on days 0 and 7 to serve as negative controls. Mice were euthanized four weeks after the last immunization, and the spleens were collected. Single cell suspensions were prepared by passage through screens, and 2 × 106 cells were stained with a murine MHC-encoded allele kd–specific pentamer for immunodominant NP-147 epitopes-conjugated with phycoerythrin (PE) and also with an anti-CD8+ antibody-conjugated with allophycocyanin (APC) and an anti-CD19 antibody-conjugated with flouro-isothiocyanin (FITC). Flow cytometric analysis was done to identify the number of NP-147 specific CD8+ T cells. Data were collected using BD FACSCanto II (BD Bioscience, CA) and FACSDiva software was used for analysis. The data represent mean± standard deviation (SD) from six animals per group. ***; P<0.0001, compared to HAd-ΔE1E3 or PBS-HAd-HA-NP control group.
