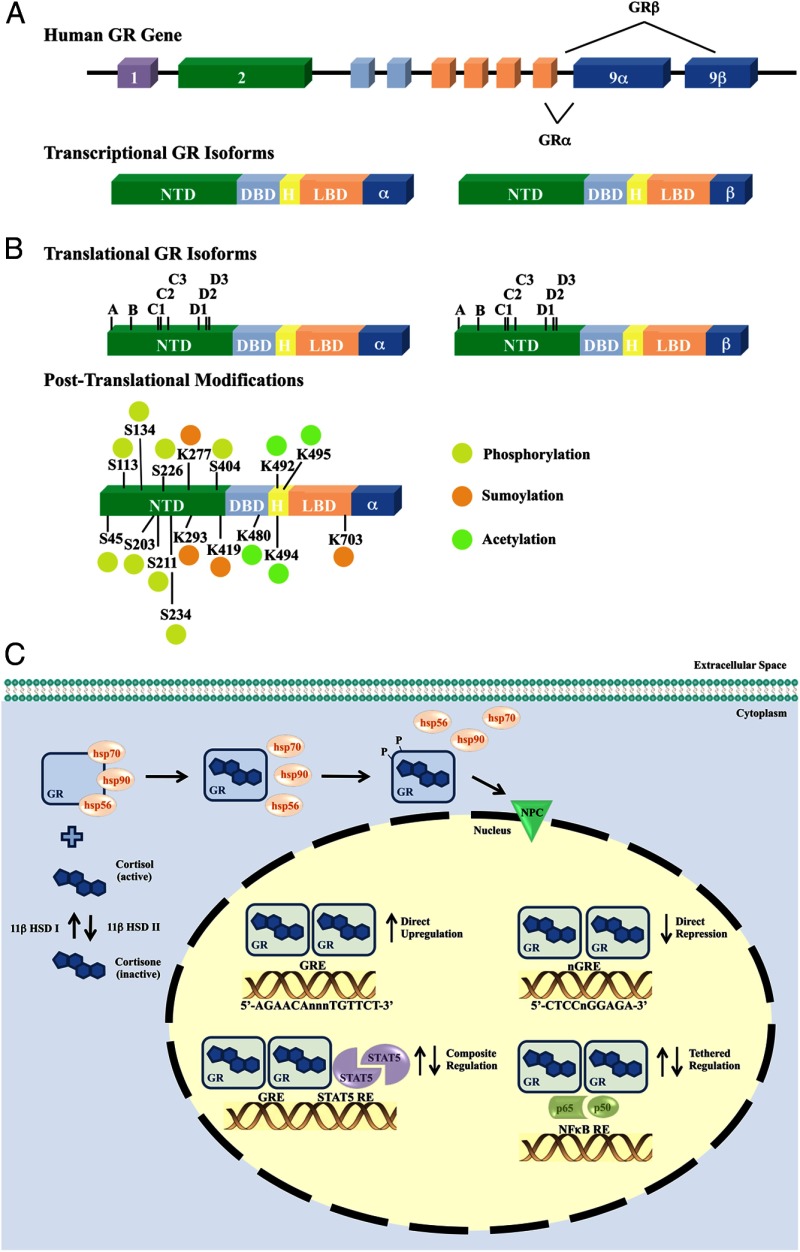
Figure 1.
Organization of and modifications to the human GR gene contribute to signaling diversity A, The human GR gene (NR3C1) is contained in one locus on chromosome 5 (5q31). Nine exons comprise the human GR primary transcript. Exon 1 forms the 5′-untranslated region, whereas exons 2–9 form the protein-coding region. Exon 2 encodes most of the NTD (N-terminal domain), exons 3 and 4 encode the DBD (DNA-binding domain), and exons 5–9 encode the hinge (H) region and LBD (ligand-binding domain). Alternative splicing of the primary transcript results in the α- and β-transcriptional human GR isoforms. B, Translational initiation at 8 different AUG start codons in a single human GR mRNA produces 8 receptor isoforms with progressively shorter NTDs (isoforms A–D3). Alternative posttranslational modifications also contribute to the diversity of human GR. Suggested and validated sites of phosphorylation (P), sumoylation (S), and acetylation (A) are indicated. C, The GR signals as a ligand-dependent transcription factor, where unliganded GR resides primarily in the cytoplasm of cells as part of a multiprotein complex. Cortisol, the most abundant natural glucocorticoid in humans, is converted from inactive cortisone by 11β-HSD I. As a mechanism for local regulation of glucocorticoid action, the biologically active form cortisol can be converted to the inactive cortisone by 11β-HSD II. Upon binding glucocorticoids, GR undergoes a conformational change, dissociates from the heterocomplex, and translocates into the nucleus. Ligand binding is also responsible for a hyperphosphorylated state of the GR protein. Once within the nucleus, GR regulates transcription of target genes by direct binding to GREs (5′-AGAACAnnnTGTTCT-3′, where “n” is any nucleotide) or nGREs (5′-CTCCnGGAGA-3′ nGRE 1, nGRE identified with variable number of spacer nucleotides 0–2), in a composite manner bound to a GRE and interacting with adjacent transcription factor binding sites (STAT5), or tethered to other transcription factors without direct DNA binding (NFκB). 11β-HSB, 11-β hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase; HSP: heat shock protein; NPC: nuclear pore complex; nGRE: negative GRE; p65: nuclear factor NF-κ-B p65 subunit; p50: nuclear factor NF-κ-B p50 subunit.