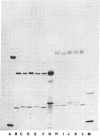
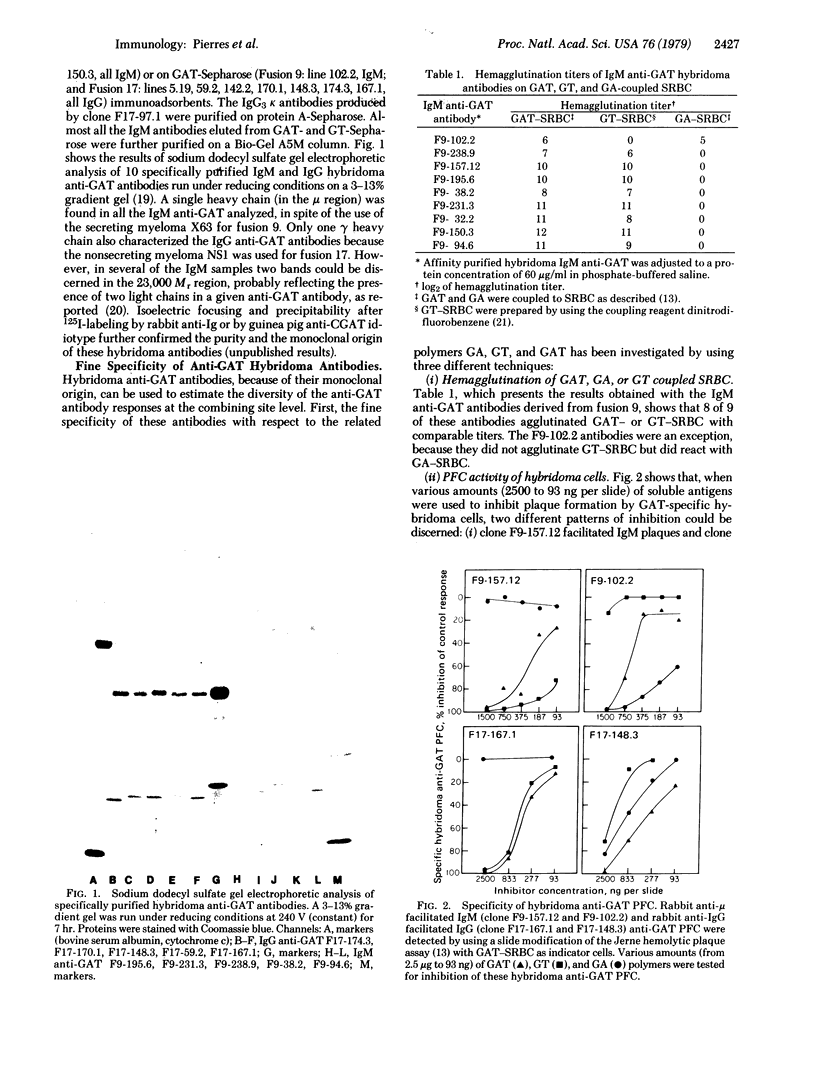
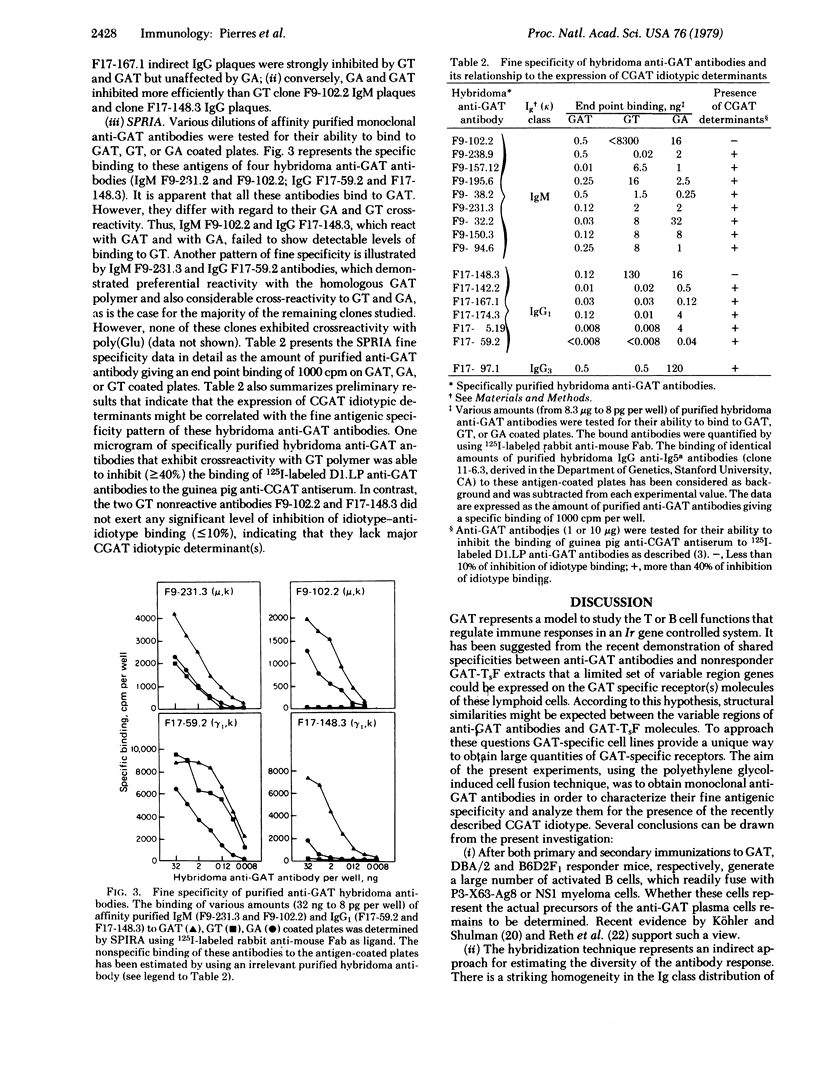
Abstract
The polyethylene glycol-mediated cell fusion technique has been used to analyze the diversity of the antibody response to the terpolymer poly(Glu60Ala30Tyr10)(GAT). Nine stable clones (all producing IgM K anti-GAT antibodies) were isolated from a fusion between P3-X63-Ag8 myeloma cells and spleen cells from a DBA/2 mouse sensitized to GAT 5 days earlier. Seven other clones (producing IgG K anti-GAT antibodies) were derived from another fusion between NSI myeloma cells and spleen cells of (C57BL/6 X DBA/2)F1 hybrid mice hyperimmunized with GAT. These 16 anti-GAT antibodies were grouped according to their pattern of reactivity with GAT and the two related polymers of poly(Glu60Ala40) (GA) and poly(GLU50Tyr50) (GT). Two monoclonal anti-GAT antibodies (IgM F9-102.2 and IgG F17-148.3) demonstrated crossreactivity with GA but failed to crossreact with GT determinants. In contrast, the remaining 14 hybridoma antibodies demonstrated preferential reactivity with GAT but also exhibited crossreactive binding to GT and in some cases GA. There was a correlation between the fine specificity pattern and the presence of a common anti-GAT idiotype on these antibodies. Thus, the hybridoma anti-GAT antibodies which reacted with GT shared crossreactive idiotypic determinants (CGAT) present in mouse anti-GAT immune sera. In contrast, the monoclonal F9-102.2 and F17-148.3 antibodies that failed to bind to GT lacked the major CGAT idiotypic determinants.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benacerraf B., Kapp J. A., Debré P., Pierce C. W., de la Croix F. The stimulation of specific suppressor T cells in genetic non-responder mice by linear random copolymers of L-amino acids. Transplant Rev. 1975;26:21–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb00173.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffino P., Scharff M. D. Rate of somatic mutation in immunoglobulin production by mouse myeloma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):219–223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfre G., Howe S. C., Milstein C., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. Antibodies to major histocompatibility antigens produced by hybrid cell lines. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):550–552. doi: 10.1038/266550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germain R. N., Ju S. T., Kipps T. J., Benacerraf B., Dorf M. E. Shared idiotypic determinants on antibodies and T-cell-derived suppressor factor specific for the random terpolymer L-glutamic acid60-L-alanine30-L-tyrosine10. J Exp Med. 1979 Mar 1;149(3):613–622. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.3.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelm H., Hjelm K., Sjöquist J. Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. Its isolation by affinity chromatography and its use as an immunosorbent for isolation of immunoglobulins. FEBS Lett. 1972 Nov 15;28(1):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80680-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ju S. T., Benacerraf B., Dorf M. E. Idiotypic analysis of antibodies to poly(Glu60Ala30Tyr10): interstrain and interspecies idiotypic crossreactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6192–6196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ju S. T., Dorf M. E., Benacerraf B. Idiotypic analysis of anti-GAT antibodies. III. Determinant specificity and immunoglobulin class distribution of CGAT idiotype. J Immunol. 1979 Mar;122(3):1054–1058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ju S. T., Kipps T. J., Theze J., Benacerraf B., Dorf M. E. Idiotypic analysis of anti-GAT antibodies. I. Presence of common idiotypic specificities in both responder and nonresponder mice. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):1034–1039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapp J. A., Pierce C. W., Benacerraf B. Genetic control of immune responses in vitro. I. Development of primary and secondary plaque-forming cell responses to the random terpolymer 1-glutamic acid 60-1-alanine30-1-tyrosine10 (GAT) by mouse spleen cells in vitro. J Exp Med. 1973 Nov 1;138(5):1107–1120. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.5.1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapp J. A., Pierce C. W., De la Croix F., Benacerraf B. Immunosuppressive factor(s) extracted from lymphoid cells of nonresponder mice primed with L-glutamic acid60-L-alanine30-L-tyrosine10 (GAT). J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):305–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinman N. R., Pickard A. R., Sigal N. H., Gearhart P. J., Metcalf E. S., Pierce S. K. Assessing B cell diversification by antigen receptor and precursor cell analysis. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1976 Jun-Jul;127(3-4):489–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Howe S. C., Milstein C. Fusion between immunoglobulin-secreting and nonsecreting myeloma cell lines. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Apr;6(4):292–295. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Shulman M. J. Cellular and molecular restrictions of the lymphocyte fusion. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:143–148. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LING N. R. The coupling of protein antigens to erythrocytes with difluorodinitrobenzene. Immunology. 1961 Jan;4:49–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontecorvo G. Production of mammalian somatic cell hybrids by means of polyethylene glycol treatment. Somatic Cell Genet. 1975 Oct;1(4):397–400. doi: 10.1007/BF01538671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reth M., Hämmerling G. J., Rajewsky K. Analysis of the repertoire of anti-NP antibodies in C57BL/6 mice by cell fusion. I. Characterization of antibody families in the primary and hyperimmune response. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Jun;8(6):393–400. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theze J., Kapp J. A., Benacerraf B. Immunosuppressive factor(s) extracted from lymphoid cells of nonresponder mice primed with L-glutamic acid60-L-alanine30-L-tyrosine10 (GAT) III. Immunochemical properties of the GAT-specific suppressive factor. J Exp Med. 1977 Apr 1;145(4):839–856. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.4.839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waltenbaugh C., Dessein A., Benacerraf B. Characterization of the primary IgM response to GAT and GT: conditions required for the detection of IgM antibodies. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):27–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waltenbaugh C., Thèze J., Benacerraf B. Restriction of primary responses to the IgG class and dependency of IgM responses on secondary immunization for the copolymers of L-glutamic acid, L-tyrosine, and L-alanine. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1278–1287. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]