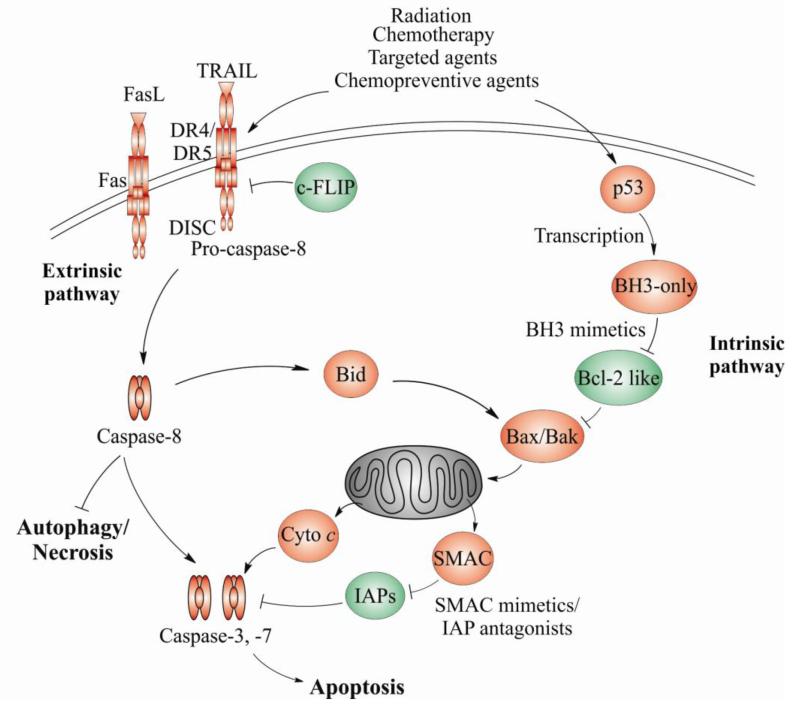
Figure 1. Coaxing cancer cells into apoptosis.
Apoptosis in mammalian cells is mediated through the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. The intrinsic pathway is predominantly regulated by the Bcl-2 family and mitochondria. The extrinsic pathway is engaged upon binding of proapoptotic ligands, such as TRAILor Fas to their respective death receptors on the cell surface. Apoptosis initiation is regulated by transcription as well as the cross-talk of two apoptotic pathways via Bid. Apoptosis is activated by anticancer agents, such as radiation, chemotherapy, kinase inhibitors, BH3 or Smac mimetics, and chemopreventive agents acting on both pathways and various players, to trigger a caspase activation cascade. Inhibition of apoptosis or certain caspases such as caspase-8 can lead to increased autophagy or necrosis, providing additional targets for drug development. Antiapoptotic proteins are colored in green while proapoptotic proteins are colored in red. Cyto c, cytochrome c.