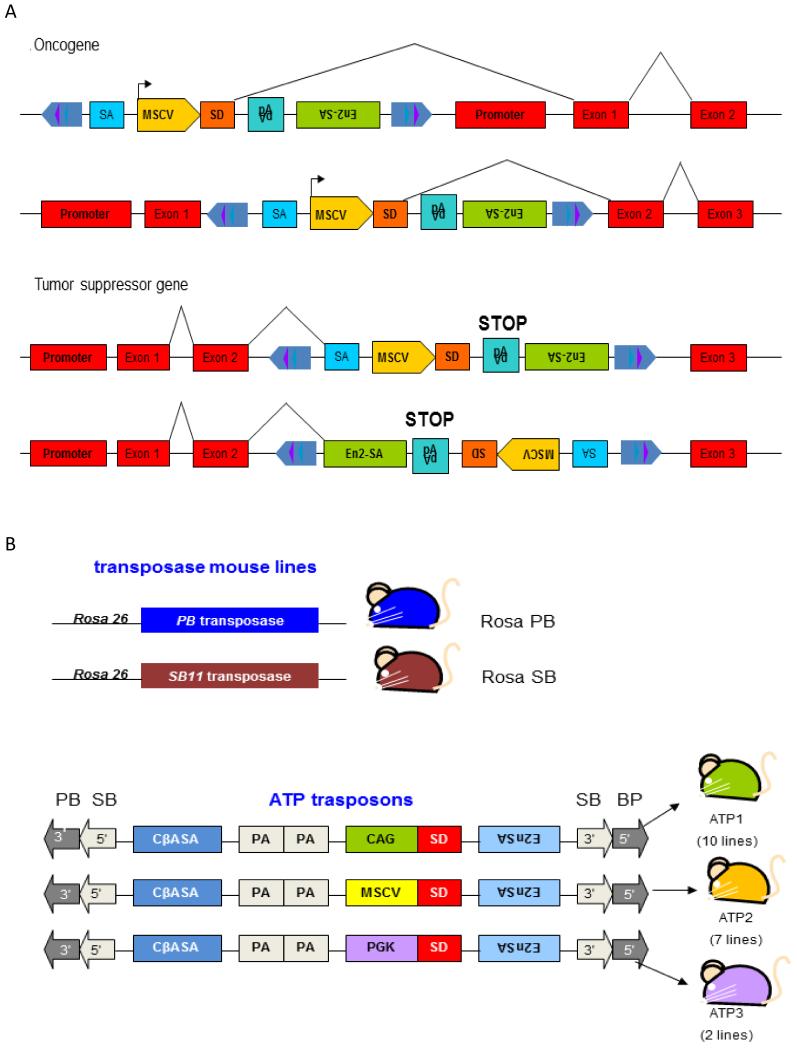
Figure 5. Transposons for insertional mutagenesis.
A) Sleeping Beauty T2/Onc2 can deregulate the expression of oncogenes or inactivate the expression of tumor suppressor genes. T2/Onc2 contains a murine stem cell virus (MSCV) 5′ long terminal repeat (LTR) and a splice donor (SD) site derived from exon 1 of the mouse Foxf2 gene. T2/Onc2 can thus promote the expression of an oncogene when integrated upstream of or within the gene in the same transcriptional orientation. T2/Onc2 is flanked by optimized SB transposase binding sites (violet and dark blue triangles) that are located within the transposon inverted terminal repeats (light blue arrows), which increase the frequency of SB transposition (upper panel). T2/Onc2 also contains two splice acceptors and a bi-directional polyA (pA) and can thus prematurely terminate transcription of a tumor suppressor gene when integrated within the tumor suppressor gene in either orientation (pale blue). One splice acceptor is derived from exon 2 of mouse engrailed 2 (En2-SA) and the other from the Carp b-actin gene (SA) (lower panel). B) The PB-based insertional mutagenesis system described in (63). Mouse lines carrying the genetic components of the transposon systems. Upper Panel: RosaPB and RosaSB knock-in mice express PiggyBac or Sleeping Beauty transposase under control of the constitutively active Rosa26 promoter. Lower panel: Transposon design and transposon mouse lines. Three transposon constructs were designed, which differ in their promoter and enhancer. All three transposons have PB as well as SB IR/DRs and can therefore be mobilized with both transposases. CβASA, Carp β-actin splice acceptor; En2SA, Engrailed-2 exon-2 splice acceptor; SD, Foxf2 exon-1 splice donor; pA, bidirectional SV40 polyadenylation signal; CAG, cytomegalovirus enhancer and chicken beta-actin promoter; MSCV, murine stem cell virus long terminal repeat; PGK, phosphoglycerate kinase promoter. Modified from (8)