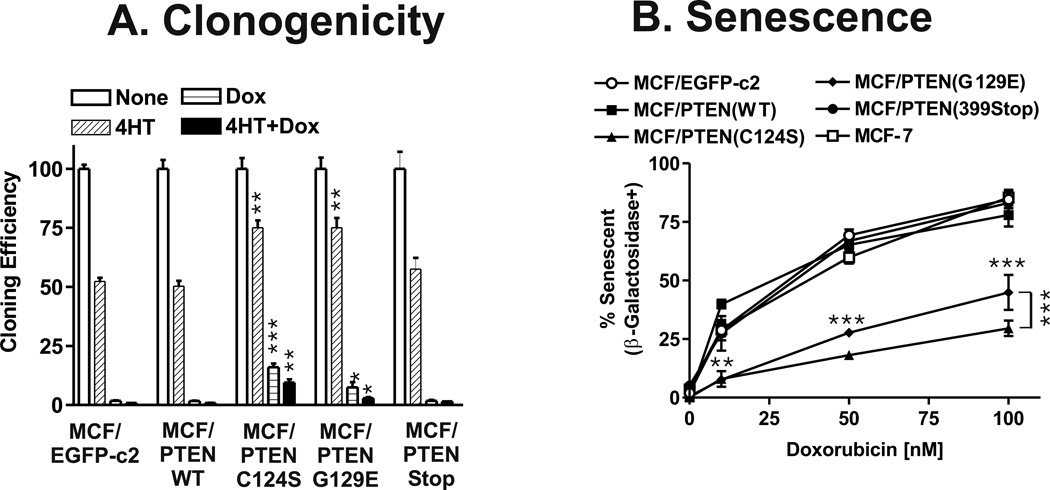
Figure 3. Effects of PTEN Mutants on Colony Formation and Cellular Senescence.
Panel A) Colony formation of PTEN transfected cells in 4HT and doxorubicin. MCF-7 cells transfected with the various PTEN plasmids were plated in triplicate in 6 well plates. The following day, the cells were exposed to 100 nM doxorubicin, 100 nM 4HT or 100 nM doxorubicin + 100 nM 4HT or no supplement. The medium was changed every three days. After 3 weeks the wells were stained with Giemsa and the number of colonies determined. The percentage colony formation was normalized to the number of colonies observed in cells not treated with 4HT, doxorubicin or 4HT + doxorubicin. The cloning efficiencies of MCF/PTEN(C124S) and MCF/PTEN(G129E) at the indicated culture conditions were statistically compared with the cloning efficiency of MCF/EGFP-c2 cells (***, P<0.001, **, P<0.005, *, P<0.05). Panel B) Effects of PTEN mutants on induction of senescence. Induction of cellular senescence was examined in the PTEN transfected cells as well as control MCF-7 and MCF/EGFP-c2 cells. The percent senescent vs. non senescent cells was determined in at least 6 fields per indicated culture condition and averaged together and the statistical significance determined by the student’s t test. The differences in induction of senescence between MCF/PTEN(C124S) and MCF/PTEN(G129E) and MCF/EGFP-c2 were statistically compared and are indicated by horizontal asterisks. The difference in induction of senescence between MCF/PTEN(C124S) and MCF/PTEN(G129E) in 100 nM doxorubicin was statistically compared and is indicated by vertical asterisks to the right of the 100 nM data points (***, P<0.001, **, P<0.005).